Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2021; 12(10):3077-3088. doi:10.7150/jca.51322 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Consumption of sugar-sweetened beverages and fruit juice and human cancer: a systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of observational studies
1. Department of Gastroenterology, The First Affiliated Hospital, Jinan University, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China.
2. Department of Information, Affiliated Hospital (Clinical College) of Xiangnan University, Chenzhou, Hunan, China.
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
Background: Several epidemiological studies have assessed the association of sugary drinks consumption with cancer, but the results remain controversial.
Objective: We performed this analysis to evaluate possible causal relationship between sugary drinks consumption and cancer risk and mortality.
Methods: We searched PubMed, Embase, and Web of Science databases in English. Observational studies evaluating the association of sugary drinks intake with cancer were included. Random-effects meta-analysis was used to calculate the risk estimates.
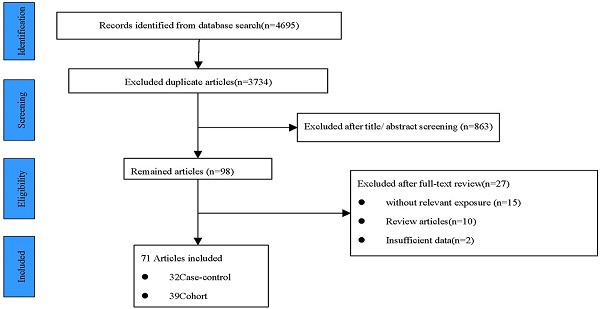
Results: A total of 71 observational articles with 32 case-control and 39 cohort studies were included in the meta-analysis. 60 addressed cancer risk, and 11 reported cancer mortality. Compared with the lowest level, the highest level of sugar-sweetened beverages (SSB) consumption showed an increased overall cancer risk (RR=1.12 95% CI: 1.06-1.19, P=0.000) and mortality (RR=1.07 95% CI: 1.01-1.14, P=0.029), and fruit juice intake showed a positive association with cancer risk in cohort studies (RR=1.06 95% CI: 1.01-1.11, P=0.013). Subgroup analyses based on cancer type indicated that risk of breast cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma, colorectal cancer, and prostatic cancer mortality had a positive association with SSB consumption. For dose-response analysis, evidence of a linear association was found between overall cancer risk and SSB or fruit juice consumption, and the risk increase by 4% for one servings/d increment in SSB intake and 14% in fruit juice.
Conclusions: Our findings suggest the consumption of sugary beverages may increase the risk and mortality of cancer, especially risk of breast cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma, colorectal cancer, and prostatic cancer, and mortality of breast cancer, though the evidence was limited.
Keywords: sugary beverages, cancer, risk, mortality, meta-analysis

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact