Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2024; 15(10):2928-2939. doi:10.7150/jca.94142 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Mendelian randomization combined with multi-omics explores the relationship between heart failure and cancer
1. Hubei provincial key laboratory of diabetic cardiovascular diseases, Xianning Medical College, Hubei University of Science and Technology, Xianning 437100, Hubei, People's Republic of China.
2. School of Basic Medical Sciences, Xianning Medical College, Hubei University of Science and Technology, Hubei University of Science and Technology, Xianning 437100, Hubei, People's Republic of China.
3. School of Pharmacy, Xianning Medical College, Hubei University of Science and Technology, Xianning 437100, Hubei, People's Republic of China.
4. School of Nuclear Technology and Chemistry & Biology, Hubei University of Science and Technology, Xianning 437100, Hubei, People's Republic of China.
Abstract
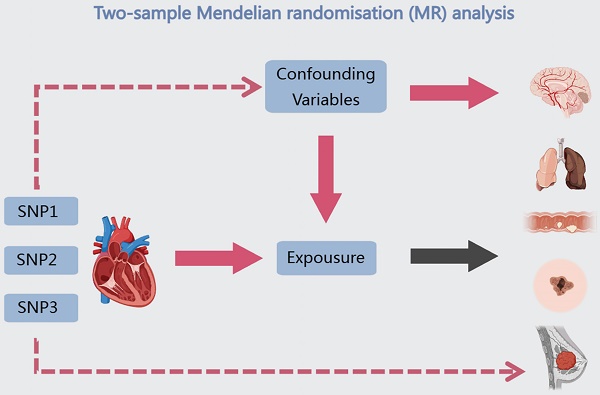
Background: Whether there is an association between HF (HF) and cancer has not been conclusively established, and it is not clear whether patients with cancer can share similar hospitalization strategies and outcomes with patients with HF.
Methods: Genome-wide association summary statistics were performed using a two-sample Mendelian randomization (MR) method for HF patients and cancer patients from the GWAS directory, with co-localization and Summary Data-Based Mendelian Randomization (SMR) analyses to identify HF-associated genes, and transcriptomic analyses to analyze the roles of these genes in the clinical diagnosis and targeted therapies of multiple cancer types.
Results: Two-sample MR analysis showed that increased risk of HF was associated with decreased risk of cervical, brain, breast, colorectal, lung, and skin cancers, and co-localization combined with SMR analysis identified ABO and SURF1 as HF-associated genes, and transcriptomic analyses showed that ABO is a risk factor for HF and a protective factor against cancer, whereas SURF1 is a protective factor against HF and a protective factor against cancer.
Conclusion: There was no causal relationship between heart failure and cancers (Cervical, brain, breast, colorectal, lung and skin cancers) risk factors, however there was a trend toward a negative causal relationship between heart failure and cancers (Cervical, brain, breast, colorectal, lung and skin cancers) occurrence.
Keywords: HF, cancer, MR, co-localisation analysis, SMR, transcriptomic analyses

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact