Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2022; 13(7):2226-2237. doi:10.7150/jca.66020 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Inducing Synergistic DNA Damage by TRIP13 and PARP1 Inhibitors Provides a Potential Treatment for Hepatocellular Carcinoma
1. School of Basic Medical Sciences &Key Laboratory of Antibody Technique of National Health Commission & Jiangsu Antibody Drug Engineering Research Center, Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing 211166, China.
2. Sir Run Run Hospital, Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing 211166, China.
3. Jiangsu Cancer Hospital & The Affiliated Cancer Hospital of Nanjing Medical University& Jiangsu Institute of Cancer Research, Nanjing 2100092, China.
4. Department of Pathology, The first people's hospital of Foshan, Foshan 528041, China
# These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
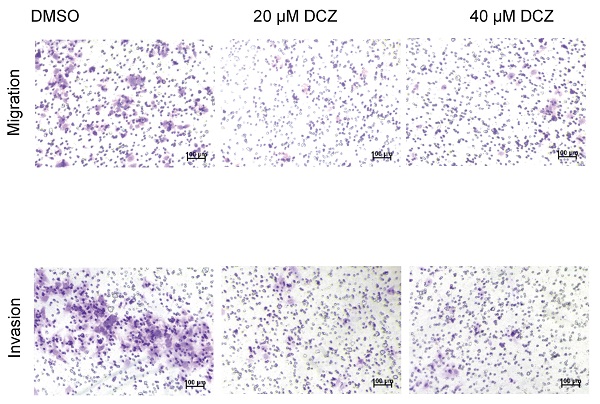
Thyroid hormone receptor interactor 13 (TRIP13), an AAA-ATPase, participates in the development of many cancers. This study explores the function of TRIP13 and synergistic effects of TRIP13 and PARP1 inhibitors in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The dose-dependent effects of TRIP13 and PARP1 inhibitors on HCC cells proliferation or migration were investigated by the CCK-8 and Transwell assays. Using siRNA or lentivirus to knock down TRIP13, we tested HCC cell and tumor growth in vitro and in vivo. The DNA damage caused by TRIP13 and PARP1 inhibitors was measured by the phosphorylation of H2AX, one of the DNA damage biomarkers. The phosphorylation of H2AX was increased after treatment with DCZ0415 or TRIP13 knockdown. Combining DCZ0415 with PARP1 inhibitor, Olaparib induced synergistic anti-HCC activity. We also found that the overexpression of TRIP13 is significantly associated with early recurrent HCC and poor survival. Up-regulation of TRIP13 in HCC was regulated by transcription factor SP1. In conclusion, our study demonstrated that DCZ0415 targeting TRIP13 impaired non-homologous end-joining repair to inhibit HCC progression and had a synergistic effect with PARP1 inhibitor Olaparib in HCC, suggesting a potential treatment of HCC.
Keywords: DCZ0415, TRIP13, H2AX, hepatocellular carcinoma, PARP1

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact