Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2022; 13(2):364-372. doi:10.7150/jca.65374 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Association of Smoking Status with Efficacy of First-line Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Advanced Non-small Cell Lung Cancers: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Department of Hematology-Oncology, Inha University College of Medicine and Hospital, Incheon, Republic of Korea.
* These authors contributed equally to this work as first authors.
Abstract
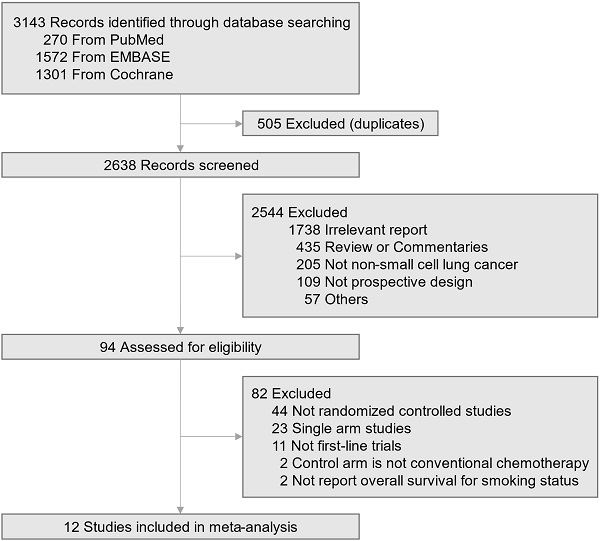
Background: Although smoking status has potential as a biomarker for immune checkpoint blockade in advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), its clinical significance remains obscure. This meta-analysis aims to assess the impact of the smoking status on the efficacy of first-line immunotherapy and to find better treatment in never-smoker and ever-smoker patients.
Methods: We searched the MEDLINE, EMBASE, and Cochrane database for trials comparing immunotherapy with conventional chemotherapy as front-line treatment for advanced NSCLC. Random-effects models were used to pool estimates of hazard ratios (HRs) for overall survival with 95% confidence intervals (CIs). Predefined subgroup analysis was performed to investigate the difference in the efficacy between the single checkpoint blockade and checkpoint inhibitor plus chemotherapy combination in the never-smokers and current/former smokers.
Results: Twelve trials involving 6,446 patients were included in the analysis. A statistically significant overall survival benefit over conventional chemotherapy was found for both checkpoint inhibitor monotherapy (HR, 0.71; 95% CI, 0.59-0.85) and checkpoint inhibitor plus chemotherapy (HR, 0.75; 95% CI, 0.63-0.90) in the current/former smoker group. There was no subgroup difference between monotherapy and combination treatment (p=0.67). However, there was an inconsistent survival outcome in the never-smoker group; checkpoint blockade monotherapy did not show significantly better efficacy than chemotherapy alone (HR, 1.05; 95% CI, 0.81-1.37), but combination treatment showed an overall survival benefit (HR, 0.64; 95% CI, 0.43-0.94). A significant subgroup difference existed between monotherapy and combination therapy (p=0.04). Similarly, there was a significant difference in efficacy of monotherapy between the current/former smoker and never-smoker group (p=0.01), but the efficacy of the combination treatment was comparable between the two groups (p=0.45).
Conclusion: Smoking status, which is easily available information, could be used as a guide in clinical practice to choose better treatment in the front-line setting for advanced NSCLC patients.
Keywords: Smoking, Non-small cell lung cancer, First-line treatment, Immune checkpoint inhibitor, Meta-analysis

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact