3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2022; 13(1):313-324. doi:10.7150/jca.64846 This issue Cite
Review
A Concise Review of MicroRNA-383: Exploring the Insights of Its Function in Tumorigenesis
1. The Central Laboratory, Shenzhen Second People's Hospital/First Affiliated Hospital of Shenzhen University Health Science Center, Shenzhen, Guangdong 518035, P.R. China.
2. Department of Physiology, School of Basic Medical Science, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou, Sichuan province 646099, P.R. China.
3. Department of Orthopedics, Shenzhen Second People's Hospital/First Affiliated Hospital of Shenzhen University Health Science Center, Shenzhen, Guangdong 518035, P.R. China.
4. Laboratory of Anesthesia and Organ Protection, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou, Sichuan province 646099, P.R. China.
#. Q.Y. and W.X. contributed equally to this review.
Abstract
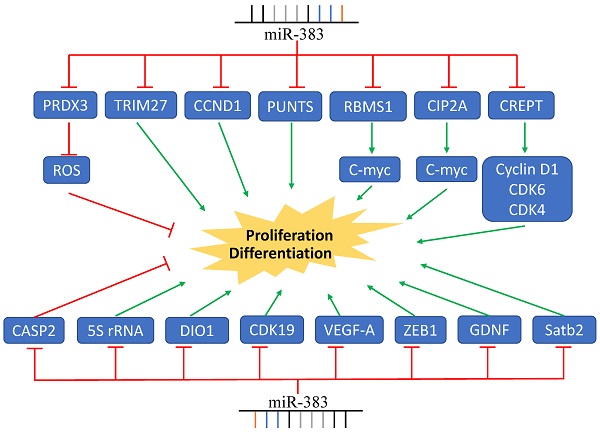
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small noncoding RNAs that commonly have 18-22 nucleotides and play important roles in the regulation of gene expression via directly binding to the 3'-UTR of target mRNAs. Approximately 50% of human genes are regulated by miRNAs and they are involved in many human diseases, including various types of cancers. Recently, microRNA-383 (miR-383) has been identified as being aberrantly expressed in multiple cancers, such as malignant melanoma, colorectal cancer, hepatocellular cancer, and glioma. Increasing evidence suggests that miR-383 participates in tumorigenic events including proliferation, apoptosis, invasion, and metastasis as well as drug resistance. Although downstream targets including CCND1, LDHA, VEGF, and IGF are illustrated to be regulated by miR-383, its roles in carcinogenesis are still ambiguous and the underlying mechanisms are still unclear. Herein, we review the latest studies on miR-383 and summarize its functions in human cancers and other diseases. The goal of this review is to provide new strategies for targeted therapy and further investigations.
Keywords: miR-383, Cancer, Proliferation, Apoptosis, Invasion, Metastasis

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact