3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2021; 12(16):4901-4911. doi:10.7150/jca.58185 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Long Noncoding RNA LIT3527 Knockdown induces Apoptosis and Autophagy through inhibiting mTOR pathway in Gastric Cancer Cells
1. Department of pharmacy, Sir Run Run Shaw Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou 310020, China.
2. Institute of Gastroenterology, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310016, China.
3. Department of Cell Biology, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou 310058, China.
Abstract
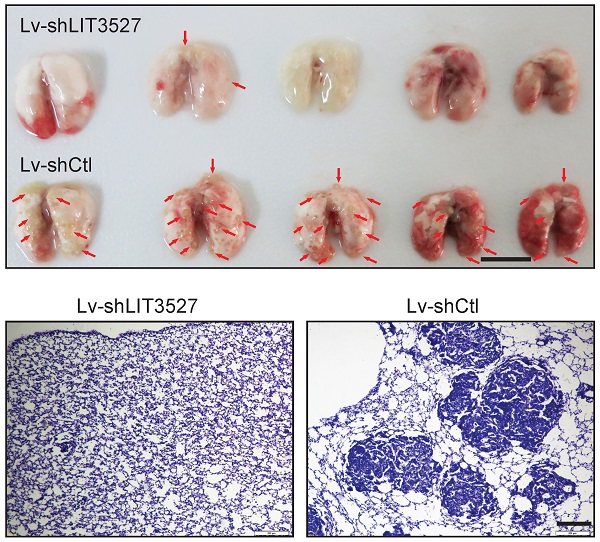
Gastric cancer is one of the most common cancers and the leading causes of cancer mortality. However, the molecular mechanisms of gastric cancer malignancy remain unclear. Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) have been well documented in controlling cancer progression. Identification of critical lncRNAs in gastric cancer will provide new sights into the regulation mechanism of gastric cancer. Here, we screened differentially expressed lncRNAs in gastric cancer tissues and matched adjacent tissues and found that lncRNA LIT3527, a 486-nucleotide (nt) sense transcript, was frequently upregulated in gastric cancer tissues. Knockdown of LIT3527 dramatically suppressed proliferation and migration of gastric cancer cells through inducing severe cell death but not affecting cell cycle. Mechanistically, we uncovered that depletion of LIT35227 induced significant cell apoptosis and autophagy through inhibiting AKT/ERK/mTOR signaling pathway. Targeting LIT3527 showed a robust inhibition of lung metastasis of gastric cancer cells. Taken together, these results suggest that LIT3527 is essential for gastric cancer cell survival through maintaining mTOR activity, suggesting that it may be clinically valuable as a therapeutic target for gastric cancer.
Keywords: lncRNA, stomach, cell cycle, cell survival, metastasis, mTOR

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact