3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2021; 12(7):1915-1925. doi:10.7150/jca.49200 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Androgen receptor (AR) decreases HCC cells migration and invasion via miR-325/ACP5 signaling
1. Department of General Surgery, Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha 410008, China.
2. Xiangya School of Medicine, Central South University, Changsha, 410013, China.
3. Department of Geriatric Surgery, Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha, 410008, China.
4. National Clinical Research Center for Geriatric Disorders, Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha, 410008, China.
5. Department of Respiratory Medicine, Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha 410008, China.
6. Key Laboratory of Biological Nanotechnology of National Health Commission, Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha 410008, China.
*first author
Abstract
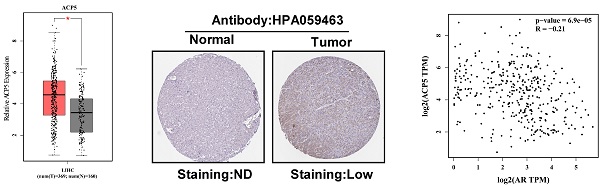
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most 5th commonly diagnosed and 2nd most lethal tumor in the world. The obvious gender advantage of HCC indicates that androgen receptor (AR) may play an important role in the tumor occurrence, develop and metastasis of HCC. Here we found that decreased AR could alter miR-325 to increase ACP5 expression in HCC cells, to increase HCC cells migration and invasion capacities. Mechanism dissection revealed that AR could regulate miR-325 expression through transcriptional regulation and miR-325 might directly target the 3'UTR of ACP5-mRNA to suppress its translation. The in vivo orthotopic xenografts mouse model with oemiR-325 also validated in vitro data. Together, these findings suggest that AR may decrease HCC progression through miR-325/ACP5 signaling and targeting the AR/miR-325/ACP5 signaling may help in the development of the novel therapies to better suppress the HCC progression.
Keywords: HCC, AR, miR-325, ACP5, migration, invasion

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact