Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2023; 14(5):741-758. doi:10.7150/jca.81811 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Identification and Validation of a Mitochondria Calcium Uptake-Related Gene Signature for Predicting Prognosis in COAD
1. Department of Cell Biology and Medical Genetics, Shanxi Medical University, Department of Hepatological Surgery, First Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan, Shanxi, China.
2. Department of Cell Biology and Medical Genetics, Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan, Shanxi, China.
3. Department of Molecular & Cellular Biology, Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center, Elm and Carlton Streets, Buffalo, NY 14263, USA.
4. Department of oncology and vascular intervention, First Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan, Shanxi, China.
#Jianjun Zhu and Wentao Zhang contributed equally to the work.
Abstract
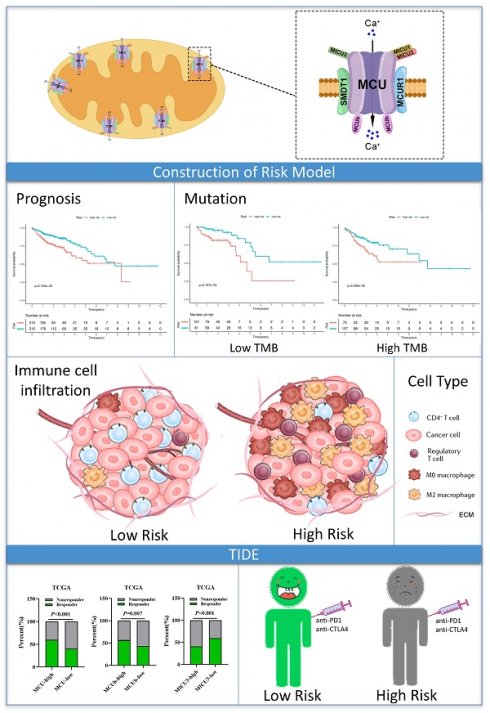
Background: Mitochondrial calcium uniporter (MCU) complex has been reported to be associated with the tumor occurrence and development in varieties of malignancies. However, the role of MCU complex in colon adenocarcinoma (COAD) remains unclear. Therefore, we constructed a risk score signature based on the MCU complex members to predict the prognosis and response to immunotherapy for patients with COAD.
Methods: The MCU complex-associated risk signature (MCUrisk) was constructed based on the expressions of MCU, MCUb, MCUR1, SMDT1, MICU1, MICU2, and MICU3 in COAD. The immune score, stromal score, tumor purity and estimate score were calculated by the ESTIMATE algorithm. We systematically evaluated the relationship among the MCUrisk, mutation signature, immune cell infiltration, and immune checkpoint molecules. The response to immunotherapy was quantified by the Tumor Immune Dysfunction and Exclusion (TIDE).
Results: Our results showed that high score of MCUrisk was a worse factor for overall survival (OS) in COAD, and MCUrisk score was significantly higher in advanced COAD. The mutation landscape was different between the MCUrisk-high and MCUrisk-low groups, and the mutation rate of TP53 was remarkably higher in MCUrisk-high group, which strongly suggested TP53 mutation might be associated with mitochondrial calcium dyshomeostasis in COAD. Furthermore, MCUrisk score was negatively correlated with tumor mutation burden (TMB), and combining risk score and TMB as a novel index was better than TMB alone in predicting the prognosis for COAD patients. The compositions of Tregs and M0/M2 macrophages were significantly increased in MCUrisk-high group, whereas CD4+ T cells was significantly decreased in MCUrisk-high group. Consistently, the immune score was lower in MCUrisk-high group. The expression levels of immune checkpoint molecules were negatively correlated with the MCUrisk score, including CD58 and CD226. Furthermore, a lower MCUrisk score indicated better response to immunotherapy, and combining risk score and immune score was a novel indicator to precisely predict the response to immuotherapy for COAD patients.
Conclusion: Altogether, a novel MCUrisk signature was constructed based on the mitochondrial calcium uptake-associated genes, and a lower MCUrisk score may predict better OS outcome and better response to immunotherapy in COAD.
Keywords: colon adenocarcinoma, gene signature, overall survival, prognosis, immunetherapy, mitochondrial calcium uniporter

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact