3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2021; 12(15):4648-4654. doi:10.7150/jca.59064 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Impact of Body Mass Index on Local Recurrence according to Intrinsic Subtype Approximation in Korean Women with Early Stage Invasive Breast Cancer Receiving Contemporary Treatments
1. Department of Radiation Oncology, Konyang University College of Medicine, Daejeon, Republic of Korea.
2. Myunggok Medical Research Institute, Konyang University College of Medicine, Daejeon, Republic of Korea.
3. Department of Radiation Oncology, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Republic of Korea.
4. Department of Surgery, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Republic of Korea.
Abstract
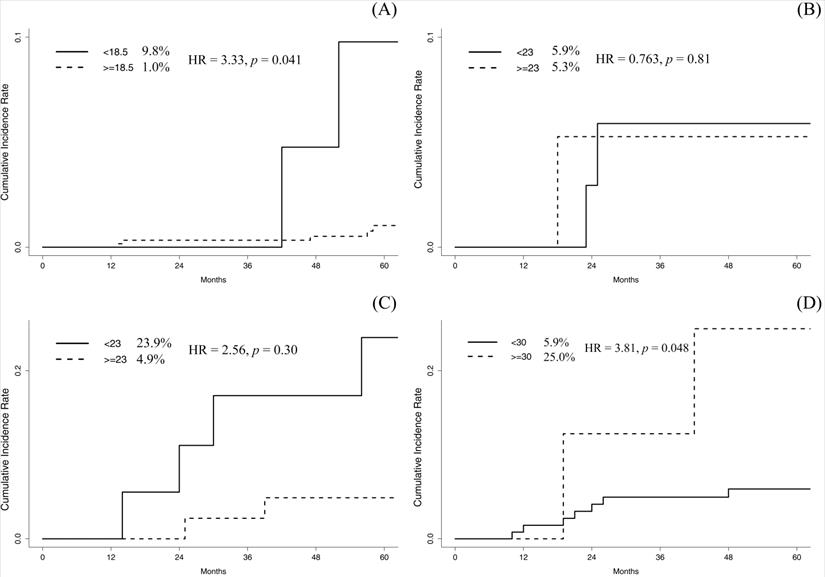
Purpose: We investigated the prognostic impact of body mass index (BMI) on local recurrence (LR) according to intrinsic subtype in Korean women with early stage, invasive breast cancer.
Materials and methods: We included 907 patients with pathological stage T1-2 and N0-1 breast cancer who underwent curative surgery between 2007 and 2012. Systemic treatments were administered in 876 patients (96.6%). In total, 701 patients (77.3%) received radiotherapy. Intrinsic subtypes were determined using immunohistochemical staining results.
Results: During the median follow-up period of 72 months, LR as the first failure occurred in 29 patients, including 24 patients with isolated LR. The 5-year cumulative incidence rate of LR was 3.2% among all patients. In the luminal A subtype, a BMI of <18.5 kg/m2 was an independent risk factor for LR, as determined by a competing-risk regression model (relative risk, 3.33; p = 0.041). Severely obese patients (BMI >30 kg/m2) with the triple negative subtype had an increased risk of LR (relative risk, 3.81; p = 0.048).
Conclusion: The present study identified traditionally underestimated risk groups for LR. BMI may diversely influence the rate of LR across intrinsic subtypes in Korean patients with breast cancer.
Keywords: breast cancer, body mass index, intrinsic subtype, local recurrence, prognostic factor

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact