3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2021; 12(10):2866-2876. doi:10.7150/jca.54408 This issue Cite
Research Paper
A Novel Immunotype-based Risk Stratification Model Predicts Postoperative Prognosis and Adjuvant TACE Benefit in Chinese Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma
1. Department of General Surgery, Comprehensive Breast Health Center, Ruijin Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai 200025, China.
2. Department of General Surgery, Qilu Hospital, Shandong University, Jinan 250012, China.
3. Department of General Surgery, Huashan Hospital & Cancer Metastasis Institute, Fudan University, Shanghai 200040, China.
4. Institute of Advanced Surgical Technology and Engineering, First Affiliated Hospital of Medical College, Xi'an Jiaotong University, Xi'an 710061, China.
* These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
Background and Aims: The tumor microenvironment can be divided into inflamed, immune-excluded and immune-desert phenotypes according to CD8+ T cell categories with differential programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-L1) expression. The study aims to construct a novel immunotype-based risk stratification model to predict postsurgical survival and adjuvant trans-arterial chemoembolization (TACE) response in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
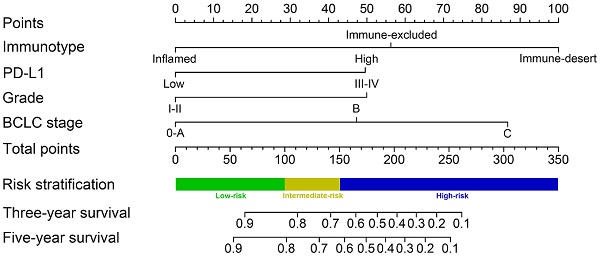
Methods: A total of 220 eligible HCC patients participated in this study. CD8+ T cell infiltration and PD-L1 expression mode were estimated by immunohistochemical staining. A risk stratification model was developed and virtualized by a nomogram that integrated these independent prognostic factors. The postoperative prognosis and adjuvant TACE benefits were evaluated with a novel immunotype-based risk stratification model.
Results: A total of 220 patients were finally identified. Immune-desert, immune-excluded, and inflamed immunotypes represented 45%, 24%, and 31% of HCC, respectively. Univariate and multivariate analyses identified immunotype and PD-L1 expression mode as independent prognostic factors for overall survival time (OS) and recurrence-free survival time (RFS). The nomogram was constructed by integrating immunotype, PD-L1 expression, Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer (BCLC) stage and tumor grade. The C-index was 0.794 in the training cohort and 0.813 in the validation cohort. A risk stratification system was constructed based on the nomogram classifying HCC patients into 3 risk groups. The average OS times in the low-risk, intermediate-risk and high-risk groups in all cohorts were 77.1 months (95% CI 71.4-82.9), 53.7 months (95% CI 48.2-59.2), and 25.6 months (95% CI 21.4-29.7), respectively. Further analysis showed that OS was significantly improved by adjuvant TACE in the low- and intermediate-risk groups (P=0.041 and P=0.010, respectively) but not in the high-risk group (P=0.398).
Conclusion: A novel immunotype-based risk stratification model was built to predict postoperative prognosis and adjuvant TACE benefit in HCC patients. These tools can assist in building a more customized method of HCC treatment.
Keywords: Hepatocellular carcinoma, adjuvant TACE, tumor microenvironment, immunotype, prognosis.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact