3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2021; 12(7):1884-1893. doi:10.7150/jca.52089 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Identification of hub genes-based predictive model in hepatocellular carcinoma by robust rank aggregation and regression analysis
1. Department of General Surgery, Sir Run-Run Shaw Hospital, School of Medicine, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, 310016, China.
2. Department of Emergency, Sir Run-Run Shaw Hospital, School of Medicine, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, 310016, China.
Abstract
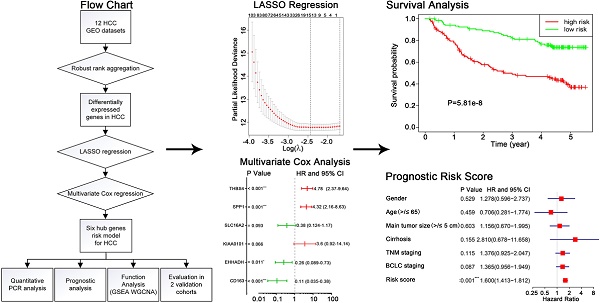
Background: Though various hub genes for HCC have been identified in decades, the limited sample size, inconsistent bioinformatic analysis methods and lacking evaluation in validation cohorts would make the results less reliable, novel biomarkers and risk model for HCC prognosis are still urgently desired.
Methods: The Robust Rank Aggression method was applied to integrate 12 HCC microarray datasets to screen for robustly and stably differentially expressed candidates. The Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator regression and multivariate Cox regression analysis were performed to construct a six hub genes-based prognostic model, which was further verified in matched tumor and non-tumor hepatic samples and two independent validation cohorts.
Results: Six hub genes for HCC were identified including CD163, EHHADH, KIAA0101, SLC16A2, SPP1 and THBS4. The risk score according to hub genes-based prognostic model could be an independent predictive factor for HCC. Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction results showed significant difference in expression level between tumor and non-tumor hepatic tissues. Prognostic value of risk model has been verified in TCGA-HCC and GSE76240 datasets. Biological function analysis revealed these hub genes were closely associated with tumorigenesis processes.
Conclusion: A novel six hub genes predictive risk model for HCC has been established based on multiple datasets analyses, providing novel features for the prediction of HCC patients' outcome.
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma, bioinformatic analysis, regression analysis, hub gene, prognostic risk model, validation dataset

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact