3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2021; 12(6):1755-1763. doi:10.7150/jca.51457 This issue Cite
Research Paper
LINC00665 promotes Ovarian Cancer progression through regulating the miRNA-34a-5p/E2F3 axis
1. Department of Gynaecology, Suzhou TCM Hospital Affiliated to Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Suzhou 215009, China.
2. Department of Gynaecology, Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing 210029, China.
3. Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing, 210023, China.
4. Department of clinical laboratory, Suzhou TCM Hospital Affiliated to Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Suzhou 215009, China.
#Co-first authors with equal contributions to this work.
Abstract
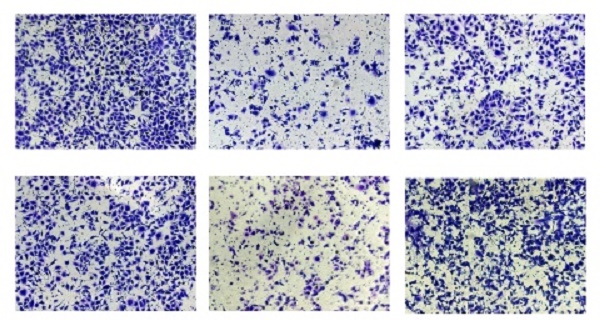
Objective: To clarify the role of LINC00665 in ovarian cancer (OC) progression and the possible mechanism.
Methods: LINC00665 levels in OC tissues and cell lines were detected by qRT-PCR. The correlation between LINC00665 and clinicopathologic characteristics of OC patients was assessed. Biological functions of OC cell phenotypes influenced by LINC00665 were examined by CCK-8, colony formation and Transwell assay. Dual-luciferase reporter assay and RIP assay were conducted to verify the interaction between LINC00665 and its downstream target.
Results: LINC00665 was upregulated in OC and linked to poor prognosis. Knockdown of LINC00665 blocked malignant proliferative, migratory and invasive functions of OC cells. By competitively binding miRNA-34a-5p, LINC00665 abolished the inhibitory effect of miR-34a-3p on its downstream gene E2F3, thus promoting OC progression.
Conclusion: LINC00665/miRNA-34a-5p/E2F3 axis is involved in OC progression, providing novel insights into the clinical treatment of OC.
Keywords: ovarian cancer, LINC00665, miRNA-34a-5p, E2F3

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact