3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2024; 15(12):3675-3683. doi:10.7150/jca.94202 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Network Pharmacology and Bioinformatics Analysis to Identify the Molecular Targets and its Biological Mechanisms of Sciadopitysin against Glioblastoma
1. Department of Neurosurgery, Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430060, P.R. China.
2. Department of Basic Medicine, Medical School, Kunming University of Science and Technology, Kunming, Yunnan, 651701, P.R. China.
3. Guangdong Key Laboratory of Genome Instability and Human Disease Prevention, Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, School of Medicine, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen, Guangdong, 518055, P.R. China.
4. Department of pediatrics, Liyuan Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, Hubei, 430077, P.R. China.
5. Department of Gynaecology and Obstetrics, Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430060, P.R. China.
Abstract
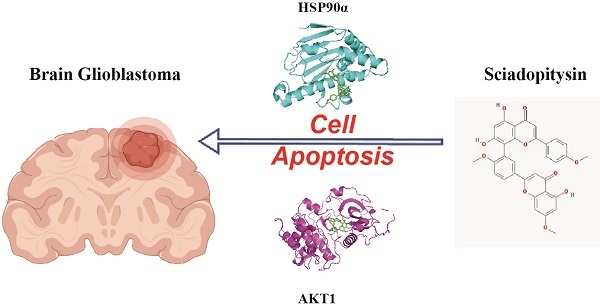
Glioblastoma multiform (GBM) is categorized as the most malignant subtype of gliomas, which comprise nearly 75% of malignant brain tumors in adults. Increasing evidence suggests that network pharmacology will be a novel method for identifying the systemic mechanism of therapeutic compounds in diseases like cancer. The present study aimed to use a network pharmacology approach to establish the predictive targets of sciadopitysin against GBM and elucidate its biological mechanisms. Firstly, targets of sciadopitysin were obtained from the SwissTargetPrediction database, and genes associated with the pathogenesis of GBM were identified from the DiGeNET database. Sixty-four correlative hits were identified as anti-glioblastoma targets of sciadopitysin. Functional enrichment and pathway analysis revealed significant biological mechanisms of the targets. Interaction of protein network and cluster analysis using STRING resulted in two crucial interacting hub genes, namely, HSP90 and AKT1. Additionally, the in vitro cytotoxic potential of sciadopitysin was assessed on GBM U87 cells. The findings indicate that the pharmacological action of sciadopitysin against GBM might be associated with the regulation of two core targets: HSP90 and AKT1. Thus, the network pharmacology undertaken in the current study established the core active targets of sciadopitysin, which may be extensively applied with further validations for treatment in GBM.
Keywords: sciadopitysin, glioblastoma, network pharmacology, HSP90, AKT1

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact