3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2024; 15(7):2066-2073. doi:10.7150/jca.91501 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Development and Validation of Deep Learning Model for Intermediate-Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma Survival with Transarterial Chemoembolization (MC-hccAI 002): a Retrospective, Multicenter, Cohort Study
1. Department of Oncology, Mengchao Hepatobiliary Hospital of Fujian Medical University, Fuzhou, Fujian, China.
2. Department of Gastroenterology, Xiamen Humanity Hospital, Xiamen, China.
3. Department of Oncology, The 900th Hospital of the People's Liberation Army Joint Service Support Force, Fuzong Clinical Medical College of Fujian Medical University, Fuzhou, Fujian, China.
4. Department of Oncology, Quanzhou First Hospital Affiliated to Fujian Medical University, Quanzhou, Fujian, China.
5. Department of Oncology, The Third Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University Yuedong Hospital, Meizhou, Guangdong, China.
6. Department of Oncology, Fujian Provincial Hospital, Fuzhou, Fujian, China.
7. Department of Oncology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University, Nanchang, Jiangxi, China.
†These authors contribute equally to the work.
Abstract
Background: There are few effective prediction models for intermediate-stage hepatocellular carcinoma (IM-HCC) patients treated with transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) to predict overall survival (OS) is available. The learning survival neural network (DeepSurv) was developed to showed a better performance than cox proportional hazards model in prediction of OS. This study aimed to develop a deep learning-based prediction model to predict individual OS.
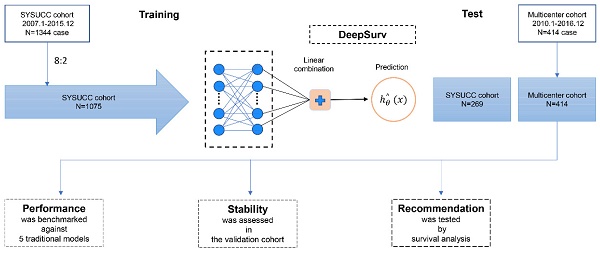
Methods: This multicenter, retrospective, cohort study examined data from the electronic medical record system of four hospitals in China between January 1, 2007, to December 31, 2016. Patients were divided into a training set(n=1075) and a test set(n=269) at a ratio of 8:2 to develop a deep learning-based algorithm (deepHAP IV). The deepHAP IV model was externally validated on an independent cohort(n=414) from the other three centers. The concordance index, the area under the receiver operator characteristic curves, and the calibration curve were used to assess the performance of the models.
Results: The deepHAP IV model had a c-index of 0.74, whereas AUROC for predicting survival outcomes of 1-, 3-, and 5-year reached 0.80, 0.76, and 0.74 in the training set. Calibration graphs showed good consistency between the actual and predicted OS in the training set and the validation cohort. Compared to the other five Cox proportional-hazards models, the model this study conducted had a better performance. Patients were finally classified into three groups by X-tile plots with predicted 3-year OS rate (low: ≤ 0.11; middle: > 0.11 and ≤ 0.35; high: >0.35).
Conclusion: The deepHAP IV model can effectively predict the OS of patients with IM-HCC, showing a better performance than previous Cox proportional hazards models.
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma, transarterial chemoembolization, deep learning model, machine learning, deepHAP IV model

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact