3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2024; 15(7):1890-1897. doi:10.7150/jca.92699 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Causal relationships between gut microbiota, immune cell, and Non-small cell lung cancer: a two-step, two-sample Mendelian randomization study
1. The Second Clinical Medical College, Zhejiang Chinese Medicine University, Hangzhou, Zhejiang 310012, China.
2. Respiratory Department, Zhejiang Jinhua Guangfu Cancer Hospital, Jinhua Zhejiang 310053, China.
3. Department of Oncology, Tongde Hospital of Zhejiang, Hangzhou, Zhejiang 310012, China.
Abstract
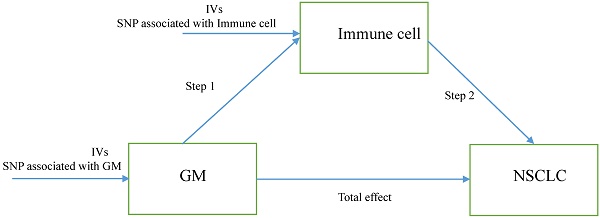
Background: Regulating the immune system is a crucial measure of gut microbiota (GM) that influences the development of diseases. The causal role of GM on Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and whether it can be mediated by immune cells is still unknown.
Methods: We performed a two-step, two-sample Mendelian randomization study with an Inverse variance weighted (IVW) approach to investigate the causal role of GM on NSCLC and the mediation effect of immune cells between the association of GM and NSCLC.
Results: MR analyses determined the protective effects of 6 genera on NSCLC (Bacteroides, Roseburia, Alistipes, Methanobrevibacter, Ruminococcus gauvreauii group, and Peptococcus). In addition, 38 immune cell traits were suggestively associated with NSCLC. Of note, the mediation MR illustrated the causal role of Genus-Peptococcus on NSCLC (Total effect IVW: OR = 0.790, 95% CI [0.657, 0.950], P = 0.012) was to a large proportion mediated by CD45 on HLA DR+ CD4+ in TBNK panel (-034 (95% CI [-0.070, -0.005]; P = 0.037), accounting for 14.4% of Total effect).
Conclusion: The study suggested a causal relationship between GM and NSCLC, which may be mediated by immune cells.
Keywords: Gut microbiota, Immune cell, Non-small cell lung cancer, Mendelian randomization

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact