3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2024; 15(6):1603-1612. doi:10.7150/jca.92968 This issue Cite
Research Paper
The METTL3/miR-196a Axis Predicts Poor Prognosis in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer
1. Department of Clinical Laboratory, Tianjin Union Medical Center of Nankai University, Tianjin 300121, China.
2. The Institute of Translational Medicine, Tianjin Union Medical Center of Nankai University, Tianjin 300121, China.
3. Department of Oncology, Tianjin Union Medical Center of Nankai University, Tianjin 300121, China.
4. Department of Thyroid and Breast Surgery, Tianjin Key Laboratory of General Surgery in Construction, Tianjin Union Medical Center of Nankai University, Tianjin 300121, China.
* These authors contribute equally to the paper.
Abstract
Background: METTL3 accelerates m6A modification to influence cancer progression including non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). To illustrate the role and underlying mechanism of METTL3 mediated miR-196a upregulation in NSCLC.
Method: The global level of m6A modification was detected by qPCR, western blot and immumohistochemical staining. The TCGA, GEPIA, CPTAC and TIMER databases were used to explore the expression change of METTL3, miR-196a and GAS7 in NSCLC patients. Kaplan-Meier analysis was performed to analyze the prognostic value of miR-196a. NSCLC cells overexpressed or knockdown miR-196a were constructed and used for CCK8, colony formation assay, western blot and immunofluorescence in vitro. The effect of miR-196a on tumor growth was investigated in vivo.
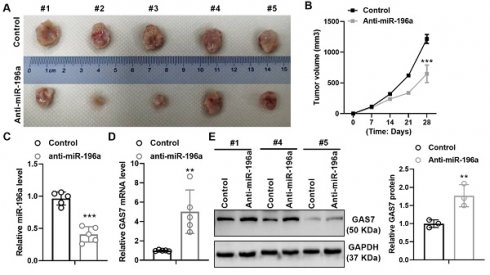
Result: We found that METTL3 mediated miR-196a were notably enhancive in NSCLC tissues and in NSCLC cells, which is markedly positively related with the serious TNM stage, the large tumor size, the distant metastasis, and the poor prognosis in patients of NSCLC. Further investigation showed that up-regulated miR-196a promoted cell viability and cell autophagy, while down-regulation of miR-196a revealed opposite results in H1299 and A549 cells. In terms of mechanism, we found that miR-196a interacted with GAS7. In addition, GAS7 expression in NSCLC patients may be positively related with the infiltration of immune cell subsets in tumor microenvironment (TME).
Conclusion: The axis of METTL3-miR-196a-GAS7 might be a target for molecular targeted therapy, a potential and novel diagnostic marker for NSCLC patients.
Keywords: METTL3, m6A, miR-196a, GAS7, NSCLC, immune cell infiltration

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact