3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2024; 15(2):332-342. doi:10.7150/jca.90149 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Causal relationship between gut microbiota and glioblastoma: a two-sample Mendelian randomization study
1. Department of Radiology, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi, 830011, China.
2. Department of Radiology, The Second Xiangya Hospital of Central South University, Changsha, Hunan, 410011, China.
# Chao Ju and Yanjing Chen contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
Background: Observational research and medical trials have suggested a connection between gut microbiota and glioblastoma, but it remains unclear if the relationship is causal.
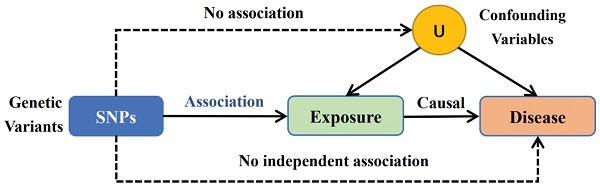
Method: A two-sample Mendelian randomization (MR) study was conducted by employing data from the MiBioGen consortium's largest genome-wide association study (n=18340) and the FinnGen consortium R8 release information (162 cases and 256,583 controls). Inverse variance weighted (IVW), weighted median estimator (WME), weighted model, MR-Egger, simple mode, and MR-PRESSO were used to determine the causal relationship between gut microbiota and glioblastoma. Reverse MR analysis was also performed on bacteria identified as causally related to glioblastoma.
Results: Seven causal relationships were identified between genetic liability in the gut microbiota and glioblastoma, involving various bacterial families and genera. No significant causal effect was found on gut microbiota from glioblastoma, and no significant heterogeneity of instrumental variables (IVs) or horizontal pleiotropy was observed.
Conclusion: A two-sample MR analysis reveals a causal association between the gut microbiota and glioblastoma, highlighting the need for more investigation to comprehend the processes behind this association.
Keywords: Gut microbiota, glioblastoma, Mendelian randomization, Genetics, SNPs

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact