3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2023; 14(14):2633-2643. doi:10.7150/jca.86739 This issue Cite
Research Paper
SEMA4A promotes prostate cancer invasion: involvement of tumor microenvironment
1. Department of Oncology, Zibo Central Hospital, Zibo, China.
2. Department of Pathology, Huazhong University of Science and Technology Union Shenzhen Hospital, Shenzhen, China.
3. Institute of Radiation Medicine, Shandong First Medical University, Shandong Academy of Medical Sciences, Jinan, China.
4. The Key Laboratory of Experimental Teratology, Ministry of Education and Department of Pathology, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Shandong University, Jinan, China.
5. Department of Radiation Oncology, Shandong Cancer Hospital and Institute, Shandong First Medical University and Shandong Academy of Medical Sciences, Jinan, China.
6. Biomedical Sciences College & Shandong Medicinal Biotechnology Centre, NHC Key Laboratory of Biotechnology Drugs, Key Lab for Rare & Uncommon Diseases of Shandong Province, Shandong First Medical University & Shandong Academy of Medical Sciences, Jinan, China.
7. Department of Radiation Oncology, Qilu Hospital, Cheeloo College of Medicine, Shandong University, Jinan, China.
Abstract
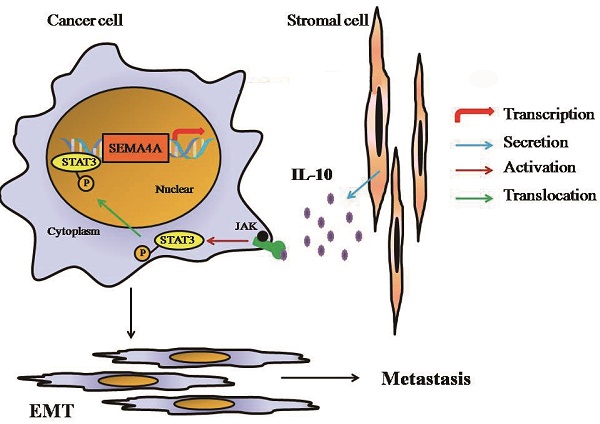
Semaphorin 4A (SEMA4A) belonged to a family of membrane-bound proteins that were initially recognized as a kind of axon guidance factors in nervous system. It was preferentially expressed on immune cells and has been proven to play a prominent role in immune function and angiogenesis. In this study, we found that SEMA4A was highly expressed in prostate cancer (PCa) tissues and correlated with Gleason scores and distant metastasis. SEMA4A could induce Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) of PCa cells and consequently promote invasion by establishing a positive loop with IL-10 in stromal cells. In vivo experiments showed more dissemination in mice injected with SEMA4A-overexpressing cells in mouse models and both the number and size of lung metastases were significantly increased in SEMA4A-overexpressing tumors. SEMA4A depletion by genetic means prevents lung metastasis in PCa xenograft models. Our data suggest a crucial role of SEMA4A in PCa and blocking SEMA4A-IL-10 axis represents an attractive approach to improving therapeutic outcomes.
Keywords: prostate cancer, SEMA4A (Semaphorin 4A), IL-10 (Interleukin-10), epithelial-mesenchymal transition, invasion, stromal

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact