3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2023; 14(14):2619-2632. doi:10.7150/jca.87411 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Validation the role of desmocollin-2 in osteosarcoma based on single cell and bulk RNA seq and experimental analyses
1. Department of Spinal Surgery, The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University, Nanning, 530021, Guangxi, China.
2. Department of Traumatic Surgery & Microsurgery & Hand Surgery, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region People's Hospital, Nanning, 530021, Guangxi, China.
3. Department of Orthopaedics, The Affiliated Yuebei People's Hospital of Shantou University Medical College, Shaoguan, Guangdong Province, China.
#Jiaxing Zeng and Yu Sun contributed equally to this work and should be considered co-first authors.
Abstract
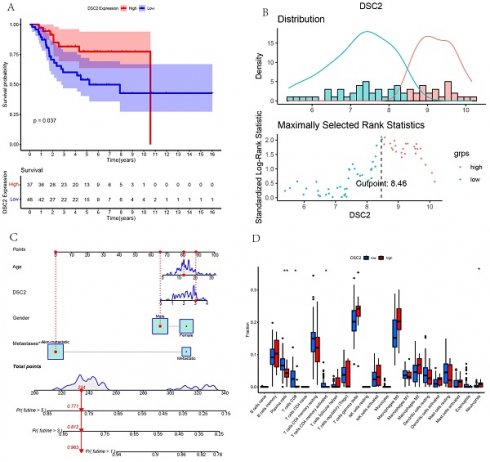
Background: The aetiology of osteosarcoma (OS) remains unclear. Desmocollin-2 (DSC2) mediates intercellular adhesion and is involved in tumour progression. Therefore, we aim to investigate the potential role of DSC2 in OS.
Methods: We analyzed the expression, prognostic value and immune infiltration of DSC2 in OS via single cell and bulk RNA seq data. Besides, the expression and function of DSC2 in OS were further verified by in vitro experiment.
Results: We preliminarily determined that DSC2 was high expressed in OS, which was a risk factor for survival and had a strong relationship with immune cell infiltration. What's more, in vitro experiments also demonstrated that DSC2 was high expressed in OS cells, and silencing DSC2 would suppress proliferation, migration and invasion of OS cells.
Conclusions: DSC2 may serve as an oncogene, which exerts a crucial role in tumor progression, predicting prognosis and immune cell infiltration in OS.
Keywords: osteosarcoma, DSC2, intercellular adhesion, biological function, molecular mechanism

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact