3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2023; 14(6):966-980. doi:10.7150/jca.80456 This issue Cite
Review
Advances in the Mechanism of Luteolin against Hepatocellular Carcinoma Based on Bioinformatics and Network Pharmacology
1. The Affiliated People's Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical University/Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region Cancer Hospital, Hohhot 010050, China.
2. Department of Pharmacy, Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010110, China.
3. Department of Pharmacy, Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, Hohhot 010020, China.
4. Department of Medicine, Ordos Institute of Technology, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, Ordos 017000, China.
5. Department of Urology, The Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010050, China.
# These authors are equal contributors to this review.
Abstract
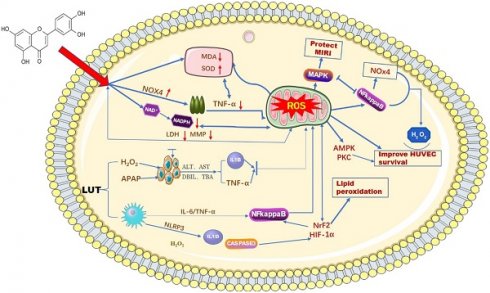
As one of the most common malignant tumors, hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) has a rising incidence rate and also seriously endangers human life and health. According to research reports, hepatitis B, hepatitis C, intake of aflatoxin in the diet, and the effects of alcohol and other chemicals can induce an increase in the incidence of liver cancer. However, in the current clinical treatment of HCC, most of the drugs are chemical drugs, which have relatively large side effects and are prone to drug resistance. Therefore, the development of natural compounds to treat HCC has become a new treatment strategy. Several studies have shown that flavonoids have shown outstanding effects and exhibit strong tumor growth inhibitory effects in vivo experimental studies. Luteolin, as a natural flavonoid, has anti-tumor, anti-inflammatory, anti-viral, anti-oxidation, immune regulation, and other pharmacological effects. The anti-cancer mechanism of luteolin mainly directly acts on tumor cells to inhibit their growth, induce cell apoptosis, reduce tumor tissue angiogenesis, regulate long non-coding RNA, affect immunogenic cell death, and regulate autophagy. As well as improving the curative effect of radiotherapy and chemotherapy and chemoprevention. In this study, we evaluated the function of luteolin in regulating cancer cell proliferation, migration, and invasion will summarize and analyze luteolin and its mechanism of regulating HCC to improve the role of luteolin in the clinical prevention and treatment of HCC.
Keywords: Luteolin, Hepatocellular carcinoma, Flavonoids, Mechanism

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact