3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2023; 14(5):784-792. doi:10.7150/jca.78423 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Role of DEP domain-containing protein 1B (DEPDC1B) in epithelial ovarian cancer
1. Department of Pathology, Affiliated Tumor Hospital of Nantong University, Nantong 226361, China
2. Department of Gynecologic Oncology, Affiliated Tumor Hospital of Nantong University, Nantong 226361, China
* Yaxun Wu, Haibing Yin and Xingsong Zhang have contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
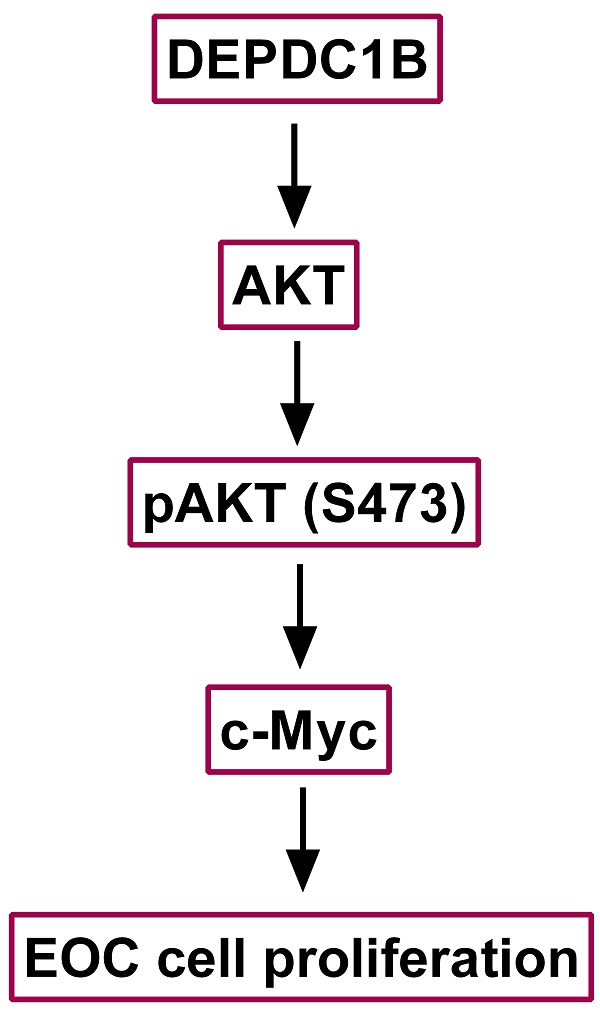
Aberrant expression of DEPDC1B (DEP domain-containing protein 1B) has been shown to be associated with various types of malignant tumors. However, little is known about the role of DEPDC1B in epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC). The purpose of this study was to investigate the expression and role of DEPDC1B in EOC. Immunohistochemical staining of 60 high-grade serous ovarian cancer (HGSOC) showed that DEPDC1B expression was associated with response to first line chemotherapy, and DEPDC1B expression was higher in platinum-resistant patients than in platinum-sensitive patients. However, there was no association between DEPDC1B expression and age, preoperative CA125 level, ascites status, location, FIGO stage, and residual disease. Furthermore, our study demonstrated that increased DEPDC1B expression was correlated with reduced overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS) time in patients with HGSOC. Multivariate analysis showed that DEPDC1B independently predicted OS in patients with HGSOC. However, DEPDC1B expression was not an independent prognostic factor for PFS in patients with HGSOC. Moreover, our study demonstrated that DEPDC1B could promote the proliferation of OVCAR3 and SKOV3 cells by enhancing AKT phosphorylation at Ser473. Treatment with MK2206 and LY294002 significantly suppressed cell proliferation that is induced by DEPDC1B up-regulation in both OVCAR3 and SKOV3 cells. Together, these results revealed that DEPDC1B was an independent prognostic factor for OS in patients with HGSOC, and DEPDC1B may promote the proliferation of EOC cells via enhancing AKT phosphorylation at Ser473.
Keywords: epithelial ovarian cancer, DEPDC1B, overall survival, progression-free survival, cell proliferation

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact