3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2022; 13(15):3598-3605. doi:10.7150/jca.67569 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Bcl-6-dependent risk stratification by nuclear expression of Peli1 in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
1. Department of Pathology, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, South Korea
2. Department of Pathology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, South Korea
3. Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, South Korea
4. Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, South Korea
Abstract
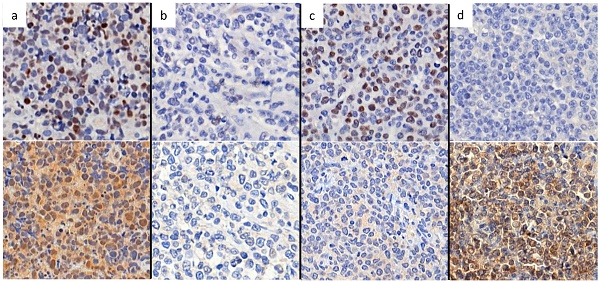
Background/Aim: Peli1 is an E3 ubiquitin ligase involving lymphomagenesis by lysine 63 ubiquitination-mediated stabilization of Bcl-6 with in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL).
Materials and Methods: We categorized nuclear expression of Peli1 according to Bcl-6 status by immunohistochemistry in DLBCL (n=100), and analyzed clinicopathologic association with prognosis.
Results: We established Bcl-6/Peli1 risk model composed of high risk (Bcl-6+/Peli1+ or Bcl-6-/Peli1-; n=64) and low risk (Bcl-6+/Peli1- or Bcl-6-/Peli1+; n=36). High risk group had more frequent non-GCB subtype (83% vs 64%; p=0.033) and Bcl-6-negativity (69% vs 28%; p<0.001) than low risk group. Univariate survival analysis for progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) revealed Bcl-6/Peli1 risk group (p=0.026 and p=0.021) and other conventional variables including international prognostic index (IPI), stage, ECOG performance status, number of extranodal sites were significant prognostic factors, along with B symptoms for OS. In multivariate analysis for PFS, Bcl-6/Peli1 risk group (p=0.032; HR=3.29), IPI (p=0.013; HR=3.39) and ECOG PS (p=0.035; HR=3.08) were independent prognostic factors. In multivariate analysis for OS, Bcl-6/Peli1 risk group (p=0.048; HR=7.87) and IPI (p=0.001; HR=12.15) were associated with prognosis.
Conclusions: DLBCL had distinctive risk groups according to pairs of nuclear Peli1 and Bcl-6 expression. These results suggest the potential role of Peli1 and Bcl-6 in risk assessment in DLBCL.
Keywords: malignant lymphoma, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, Bcl-6, Peli1

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact