3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2022; 13(6):1895-1904. doi:10.7150/jca.60269 This issue Cite
Research Paper
MiR-211-5p Inhibits the Biological Behaviors of Colorectal Cancer via SPARC-Related Growth Factor Pathways
1. Department of Clinical Laboratory, Henan Provincial People's Hospital, People's Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, Henan, 450003, P. R. China.
2. Department of Pathology, Affiliated Tumor Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, Henan, 450008, P. R. China.
Abstract
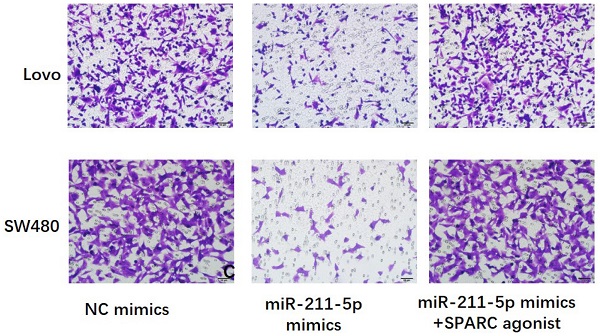
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is a highly malignant cancer with poor prognosis. MiR-211-5p has been widely studied as an antioncogene; however, its function and mechanism in CRC are still unknown. This study aimed to investigate the expression patterns and biological implications of miR-211-5p in CRC. This study used quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction to evaluate miR-211-5p expression in CRC cells and tissues. MiR-211-5p mimics were constructed to overexpress miR-211-5p in Lovo and SW480 cells. Tumor bioactivities of CRC, including cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and colony formation, were evaluated. The dual-luciferase assay was used to confirm the targeted relationship between miR-211-5p expression and secreted protein acidic and rich in cysteine (SPARC). In addition, Western blot analysis and immunohistochemical staining were used to measure SPARC, platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), transforming growth factor β (TGF-β), and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression levels. This study showed downregulated miR-211-5p expression in CRC cells and tissues, and this downregulation correlated with CRC progression. Meanwhile, miR-211-5p restrained CRC cell proliferation, colony formation, migration, and invasion. Mechanistically, SPARC-related growth factor pathways, including VEGF, PDGF, and TGF-β pathways, were upregulated in CRC tissues. Furthermore, SPARC acted as the target gene for miR-211-5p. Finally, SPARC overexpression suppressed the inhibitory effect of miR-211-5p on CRC cell progression. MiR-211-5p suppressed the invasion, migration, proliferation, and progression of CRC cells through sponging SPARC-related growth factor pathways.
Keywords: colorectal cancer, growth factors, invasion, miR-211-5p, SPARC

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact