3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2022; 13(5):1685-1694. doi:10.7150/jca.69278 This issue Cite
Review
Tumor-derived exosomes in hypoxic microenvironment: release mechanism, biological function and clinical application
1. Department of Burn and Plastic Surgery-Hand Surgery, First People's Hospital of Changshu City, Changshu Hospital Affiliated to Soochow University, Soochow, China.
2. College of Pharmaceutical Science, Soochow University, Soochow, China.
3. Department of General Surgery, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Fujian Medical University, Quanzhou, China.
4. Department of General Surgery, First People's Hospital of Changshu City, Changshu Hospital Affiliated to Soochow University, Soochow, China.
Abstract
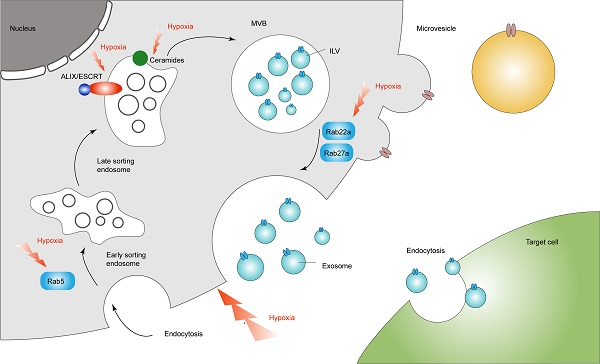
Hypoxia is a key feature of solid tumors and is related to disease aggressiveness and adverse outcomes. It is recognized that the two-way communication between cancer cells and their microenvironment is critical to cancer progression. Increasing evidences show that the cellular communication and crosstalk between tumor cells and their microenvironment is not limited to secreted molecules, but also includes exosomes secreted by tumor cells. Exosomes are nano-scale extracellular vesicles (30-100 nm in diameter), which carry the molecular characteristics and cargo of the source cell, participating in intercellular communication through autocrine, paracrine and near-crine pathways. Recent studies have shown that cancer cells produce more exosomes under hypoxic conditions than normoxia conditions. The secretion and function of exosomes could be influenced by hypoxia in various types of cancer. Therefore, in this review, we summarize and discuss the latest research on the physiological mechanism of hypoxia regulating the secretion of exosomes, and the involvement of hypoxic exosomes in cancer progression and immune escape processes, and expounds the potential for targeting hypoxia-induced exosomes for cancer therapy strategies.
Keywords: Hypoxic microenvironment, Cancer, Exosomes, Biological functions, Cancer therapy

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact