3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2022; 13(5):1523-1529. doi:10.7150/jca.69130 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Investigating factors associated to dysphagia and need for percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy in patients with head and neck cancer receiving radiation therapy
1. Department of Radiation Oncology, Papageorgiou Hospital, Thessaloniki, Greece
2. Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, 1 st University Surgery Department, Papageorgiou Hospital, Thessaloniki, Greece
3. Medical Oncology Department, Papageorgiou Hospital, Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, Greece
4. Diagnostic Medical Center, Thessaloniki, Greece
5. Section of Statistics and Operational Research, Department of Mathematics, Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, Greece
Abstract
Purpose: In this study we sought to investigate factors associated to dysphagia and subsequent need for percutaneous gastrostomy (PEG) usage, in patients with head and neck cancer receiving radiation therapy.
Methods: The records of 123 patients with non-metastatic, stage I-IV head and neck cancer who were submitted to radiation therapy were retrospectively reviewed. Logistic regression models were used to investigate for associations between the outcomes of interest (grade ≥2 dysphagia and need for [PEG] usage) and potential predictive factors.
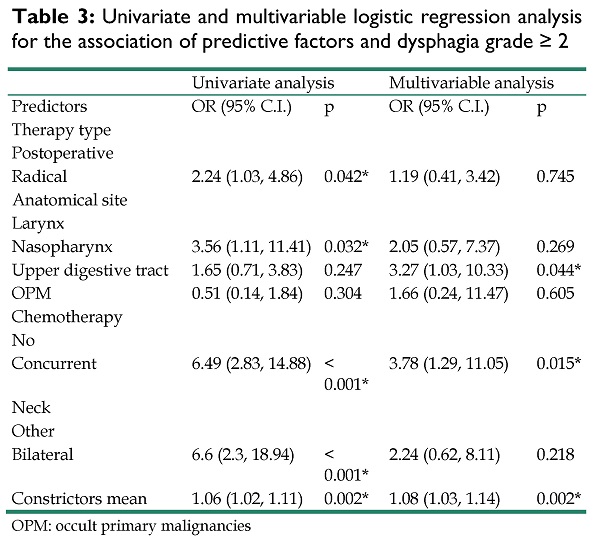
Results: Mean dose to pharyngeal constrictor muscles (OR=1.08, p=.002), concurrent chemotherapy (OR=3.78, p=0.015) and upper aerodigestive tract malignancies (OR=3.27, p=0.044) were associated with dysphagia grade≥2. A threshold of constrictors mean dose for dysphagia manifestation was also identified at 43 Gy (OR=4.51, p=0.002). Need for PEG use was correlated with definitive treatment (OR=7.03, p=.022), nasopharyngeal (OR=12.62, p=0.003), upper aerodigestive tract (OR=9.12, p=0.007) or occult primary malignancies (OR=10.78, p=0.016).
Conclusion: Patients suffering from upper aerodigestive tract malignancies, those with calculated constrictors mean dose >43 Gy, or planned to receive concurrent chemotherapy-radiotherapy should be closely monitored during treatment for dysphagia manifestation. Prophylactic PEG could be considered for patients receiving definitive therapy of the nasopharynx, upper aerodigestive tract or occult primary malignancies.
Keywords: toxicity, radiotherapy, dysphagia, cancer

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact