3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2022; 13(1):134-145. doi:10.7150/jca.51854 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Gastrin/CCK-B Receptor Signaling Promotes Cell Invasion and Metastasis by Upregulating MMP-2 and VEGF Expression in Gastric Cancer
Key Laboratory of Endemic and Ethnic Diseases, Ministry of Education and Key Laboratory of Medical Molecular Biology, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang, Guizhou, China.
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
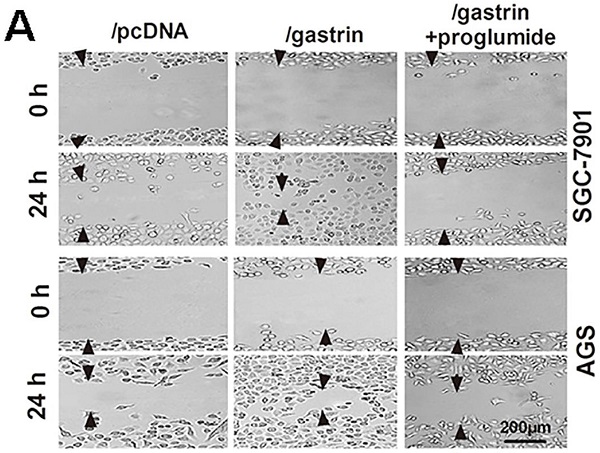
Accumulated evidence suggests that a functional loop composed of gastrin and cholecystokinin B receptor (CCK-BR) may exist in gastric carcinogenesis. However, this suggestion is not completely supported due to a lack of direct evidence, and the underlying mechanism is not completely understood. Here, we evaluated the effects of gastrin/CCK-BR signaling on the cell growth, invasion, and expression of MMP-2 and VEGF, as well as xenograft growth in vivo. Furthermore, we detected gastrin mRNA content in human gastric cancer tissues, metastatic lymph nodes, and adjacent nontumor tissues. We found that the forced gastrin could promote the proliferation, migration, and invasion of gastric cancer cells by upregulating the expression of MMP-2 and VEGF. Blocking gastrin/CCK-BR signal using either Proglumide, a CCK-BR antagonist, or shRNA against GASTRIN significantly inhibited the gastrin-promoting effects. In vivo study revealed that the tumor growth in nude mice inoculated with gastrin-overexpressed cells was significantly faster than control cells. The gastrin mRNA content in metastatic lymph nodes was higher in patients with gastric cancer than in primary gastric cancer and adjacent nontumor tissues. In conclusion, we provided direct evidence and possible mechanism of gastrin/CCK-BR signaling in the initiation and progression of gastric cancer.
Keywords: Gastrin, Cholecystokinin B receptor, Gastric cancer, MMP-2, VEGF

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact