3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2021; 12(22):6610-6619. doi:10.7150/jca.58500 This issue Cite
Research Paper
FIN56, a novel ferroptosis inducer, triggers lysosomal membrane permeabilization in a TFEB-dependent manner in glioblastoma
1. Department of Neurosurgery, Qilu Hospital of Shandong University and Institute of Brain and Brain-Inspired Science, Shandong University, Jinan, China.
2. Shandong Key Laboratory of Brain Function Remodeling, Jinan, China.
3. Department of Neurosurgery, Heze third people's hospital, Heze, China.
Abstract
Objective: To explore the anti-tumor effect of FIN56, a novel ferroptosis inducer, on glioblastoma and its underlying mechanisms.
Methods: Two human glioblastoma cell lines, LN229 and U118 were applied in this study. Anti-tumor effect was measured by CCK-8 assay, EdU assay and cell cycle analysis. Fluorescent probes, immunofluorescence, plasmid transfection, shRNA knocking out, reverse transcription PCR, western blot analysis, and transmission electron microscopy were used to study the underlying mechanisms. At last, a subcutaneous nude mice model was used to study the anti-tumor effect of FIN56 in vivo. The GraphPad Prism software program was applied for statistical analysis.
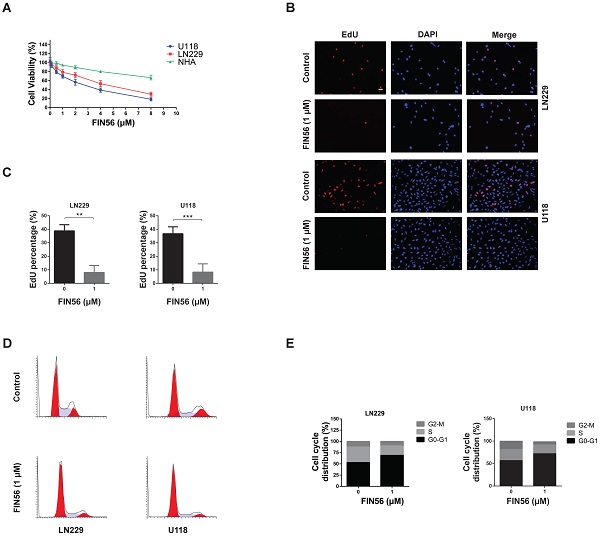
Results: FIN56 decreased cell viability, inhibited cell proliferation and caused cell cycle arrest on LN229 and U118 cells. Further study showed that FIN56 induced ferroptosis and induced lysosomal membrane permeabilization in a ferroptosis and transfactor EB dependent manner. Animal study demonstrated that FIN56 inhibited glioma growth and caused ferroptosis in vivo.
Conclusion: FIN56 is a promising anti-tumor compound.
Keywords: FIN56, Ferroptosis, Lysosomal membrane permeabilization, Glioblastoma

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact