3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2021; 12(16):4810-4818. doi:10.7150/jca.57819 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Prognostic significance of miR-203 and ZEB1 expression in early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma
1. Department of General Surgery, Shandong Provincial Hospital Affiliated to Shandong First Medical University, Jinan, Shandong 250021 China.
2. Department of Gynaecology, People' Hospital of Rizhao, Rizhao, Shandong 276800 China.
3. Department of Human Anatomy and Key Laboratory of Experimental Teratology, School of Medicine, Shandong University, Jinan, Shandong 250012 China.
4. Key Laboratory of Chemical Biology (Ministry of Education), Department of Pharmacology, School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Cheeloo College of Medicine, Shandong University, Jinan, Shandong 250012 China.
Abstract
Background: Approximately one-quarter of patients with early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) suffer from tumor recurrence within the first year after hepatectomy. Identification of patients at high risk of recurrence and new therapeutic approaches are crucial to improve clinical outcome. This study aimed to assess the prognostic significance of miR-203 and Zinc finger E-box binding homeobox 1 (ZEB1) in early-stage HCC and explore the association between the expression of ZEB1 and miR-203 in HCC.
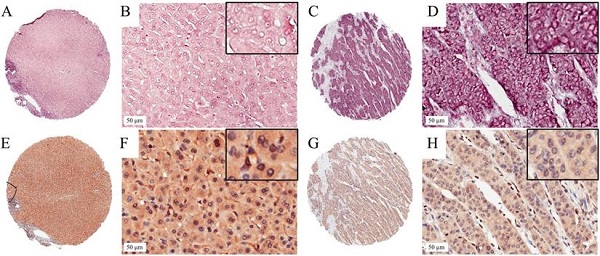
Methods: Tissue microarray-based immunohistochemistry (IHC) and in situ hybridization (ISH) were performed to investigate ZEB1 and miR-203 expression in 73 patients with early-stage HCC and their correlation with clinicopathological features and prognosis of patients were analyzed. The prognostic value of the two factors was also measured by public KM plotter database. Quantitative reverse transcription PCR (qRT-PCR) assays were conducted to study the relationship between miR-203 and ZEB1. Transwell assays, Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) assays were performed to detect the roles of miR-203 in migration, invasion and proliferation of HCC cells.
Results: We found low expression of miR-203 was associated significantly with tumor recurrence (P<0.001) and poor survival (P=0.020) of patients with early-stage HCC. Multivariate analysis revealed that low miR-203 expression was a poor prognostic factor for both overall survival (OS) (P=0.036) and recurrence free survival (RFS) (P=0.017). ZEB1 did not show any prognostic significance in our cohort. Correlation analysis indicated that there was no significant correlation between miR-203 and ZEB1 on both mRNA and protein levels. Furthermore, functional studies indicated that miR-203 repressed migration, invasion and proliferation of HCC cells in vitro.
Conclusion: Our study suggested that miR-203 could be a novel predictor in early-stage HCC and might also be a potential molecular target for HCC therapy.
Keywords: miR-203, Hepatocellular carcinoma, ZEB1, Prognosis

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact