3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2021; 12(15):4739-4744. doi:10.7150/jca.56029 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Predictive Value of Routine Blood Test in patients with Early Esophageal Cancer: A Matched Case-Control Study
Department of Gastroenterology, First Affiliated hospital of Nanjing medical university.
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
Aims: The present study was to evaluate the diagnostic value of routine blood test as potential inflammatory markers in early esophageal cancer (EEC) patients.
Methods: A matched case-control study was conducted by recruiting 314 patients who were pathologically diagnosed with EEC and then underwent Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection (ESD) from July 2015 to July 2019 in First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University. Each EEC patient was matched against one healthy control on the criteria of gender, and age (±2 years). Additionally, a total of 40 subjects (20 cases and 20 controls) were also included in the validation set. Statistical analysis of selected hematological parameters was performed between the two groups. The correlation between preoperative blood indexes and clinicopathological characteristics after ESD in EEC patients were further assessed.
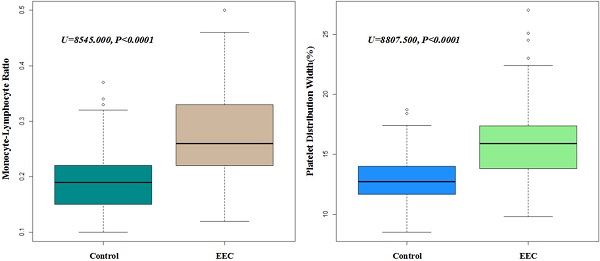
Results: Mono-factor analysis showed that the index of monocyte (p<0.001), MCV (p=0.018), MCH (p=0.01), MPV (p=0.022), PT (p=0.003), PT-INR (p=0.003), PDW (p<0.001) and MLR (p<0.001) were statistically significant in EEC patients when compared with those in healthy controls. Multivariate logistic regression analysis further identified that PDW and MLR was independently associated with the risk of early esophageal cancer (both p<0.001). The higher level of NLR (P=0.007) and MLR (P=0.015) were statistically significant with submucosal invasion in EEC patients and the level of MLR were significantly associated with larger tumor size (P=0.030). The results of the validation group were in consistence with the primary group.
Conclusions: Hematological parameters of MLR and PDW can be used as an adjuvant tool for the diagnosis of EEC. Moreover, the value of MLR can reflect the invasion depth index.
Keywords: early esophageal cancer, MLR, PDW, inflammatory index

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact