3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2021; 12(15):4478-4487. doi:10.7150/jca.55738 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Suitability of Endobronchial Ultrasound-Guided Transbronchial Needle Aspiration versus Paired Transbronchial Biopsy Specimens for Evaluating Programmed Death Ligand-1 Expression in Stage III and IV Lung Cancer: A Comparative Retrospective Study
1. Department of Respiratory Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Institute of Medical, Pharmaceutical and Health Sciences, Kanazawa University.
2. Department of Respiratory Medicine, Kanazawa University Hospital.
3. Department of Respiratory Medicine, National Hospital Organization Kanazawa Medical Center.
4. Department of Molecular and Cellular Pathology, Graduate School of Medical Science, Kanazawa University.
5. Department of Clinical Laboratory Science, Faculty of Health Sciences, Kanazawa University.
6. Department of Pathology, National Hospital Organization Kanazawa Medical Center.
Abstract
Objectives: Cancer cells usually escape tumor-reactive T-cell responses using immune checkpoint proteins, such as programmed death protein-1 (PD-1) and its ligand, programmed death ligand-1 (PD-L1). These proteins can be blocked by immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs); the decision on ICI-based first-line treatment for advanced lung cancers depends on the PD-L1 levels in tumor specimens. Determining the PD-L1 expression conventionally requires histological specimens from resected tumors and core biopsy specimens. Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is usually diagnosed at stage III or IV; therefore, only small biopsy specimens, such as those obtained via endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration (EBUS-TBNA) are available. However, the suitability of EBUS-TBNA specimens determining the PD-L1 expression levels in advanced lung cancers remains unclear.
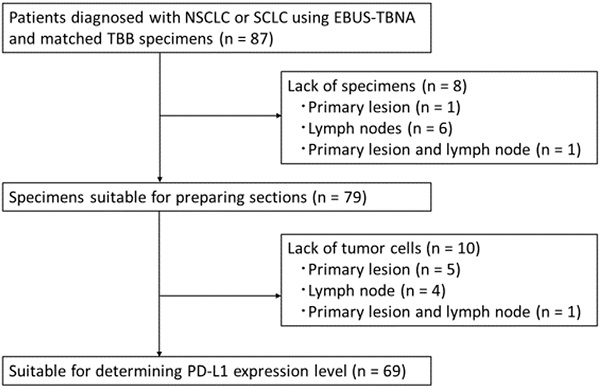
Materials and Methods: Here, we investigated the concordance rate of PD-L1 expression between EBUS-TBNA and matched transbronchial biopsy (TBB) specimens. Using the 22C3 anti-PD-L1 antibody (immunohistochemistry), we determined the PD-L1 expression levels in paired specimens obtained from 69 patients (50 with advanced NSCLC and 19 with small cell lung cancer [SCLC]), as well as the efficacy of ICIs in these patients.
Results: The concordance rate of PD-L1 expression between the EBUS-TBNA and TBB specimens was 78.3%. The κ values referent to the PD-L1-positive expression rate between EBUS-TBNA and TBB specimens were 0.707 and 0.676 at cutoff limits of ≥1% and ≥50%, respectively. Among the 19 SCLC patients, 16 (84.2%) exhibited no PD-L1 expression in both EBUS-TBNA and TBB specimens. Notably, the progression-free survival of patients with ≥50% PD-L1 expression in the paired specimens who received ICI treatment was 8.3 months.
Conclusion: Collectively, our results validate the use of EBUS-TBNA specimens for the determination of the PD-L1 expression levels in the context of NSCLC and SCLC.
Keywords: programmed death ligand-1, endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration, non-small cell lung cancer, small cell lung cancer, immune checkpoint inhibitor.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact