3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2021; 12(15):4455-4462. doi:10.7150/jca.57896 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Effect of surgical margin on postoperative prognosis in patients with solitary hepatocellular carcinoma: A propensity score matching analysis
1. Guangxi Medical University Cancer Hospital, Nanning 530021, China.
2. School of Public Health, Guangxi Medical University, Nanning 530021, China.
Zewen Zhou and Lunan Qi contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
Objective: The effect of surgical margin (SM) on the postoperative prognosis of patients with solitary hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) remains controversial. This study aimed to evaluate the effect of SM on the postoperative prognosis of patients with solitary HCC by using propensity score matching (PSM).
Methods: Patients with solitary HCC who underwent liver resection were divided into a wide margin group (1.0 cm or more, group W) and a narrow margin group (< 1.0 cm, group N). Progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) associated with the SM status and the factors influencing postoperative prognosis were evaluated.
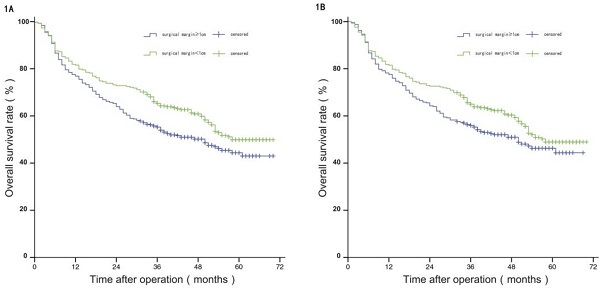
Results: Before PSM, the indicators were not balanced between the two groups. PFS and OS were significantly lower in group N than group W. The factors affecting postoperative prognosis were international normalized ratio (INR), AST, capsule integrity, microvascular invasion, tumour embolus and tumour size. After PSM, data of both groups were balanced and comparable, and no significant differences in OS or PFS between the two groups. The INR in the above affecting factors was excluded.
Conclusion: For solitary HCC patients with negative SMs, SM size does not affect prognosis. INR, AST, capsule integrity, microvascular invasion, tumour embolus and tumour size are independent factors influencing the postoperative prognosis of solitary HCC patients.
Keywords: surgical margin, postoperative prognosis, propensity score matching, hepatocellular carcinoma

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact