3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2021; 12(13):4039-4048. doi:10.7150/jca.53124 This issue Cite
Research Paper
LRP1B mutation: a novel independent prognostic factor and a predictive tumor mutation burden in hepatocellular carcinoma
1. Department of Pathology, Affiliated Hospital of Youjiang Medical University for Nationalities, Baise 533000, Guangxi, PR China.
2. Youjiang Medical University for Nationalities, Baise 533000, Guangxi, PR China.
3. Medical College of Guangxi University, Nanning, 530004, Guangxi, PR China.
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
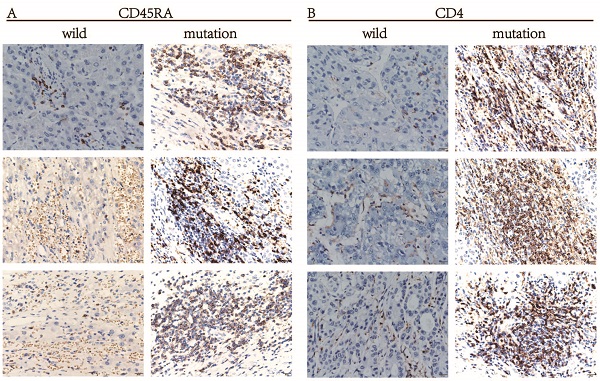
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most common malignancies globally and the second leading cause of cancer-related death. Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) receptor-related protein 1B (LRP1B) is one of the commonly mutated genes in HCC, but its role in HCC remains unclear. In this study, we analyzed the role of LRP1B mutation in HCC. The bioinformatics results show that LRP1B had a frequency of mutation in HCC patients, and LRP1B mutation was associated with a higher tumor mutation burden (TMB), and survival analysis proved that the prognosis of HCC patients with LRP1B mutation was poor. Univariate and multivariate COX regression analysis indicated that LRP1B mutation was an independent risk factor in evaluating HCC patients' prognosis. Correlation analysis showed that LRP1B mutation status was associated with the infiltration of 2 types of immune cells and higher expression of immune checkpoint gene human endogenous retrovirus-H long terminal repeat-associating protein 2 (HHLA2) in HCC patients. In summary, the results show that LRP1B mutation is associated with the higher TMB and poor prognosis of patients with HCC, and it was an independent risk factor for clinical outcomes of HCC patients. LRP1B gene mutations can serve as predictors in HCC patients with higher TMB and higher expression of HHLA2. The results of this study will be beneficial to future studies on targeted therapy and immunotherapy for HCC.
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma, bioinformatics, LRP1B, mutation, TMB, prognosis

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact