3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2021; 12(13):3958-3966. doi:10.7150/jca.53981 This issue Cite
Research Paper
CDK5 Knockdown inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis and Cell Cycle Arrest in Human Glioblastoma
1. Department of Neurosurgery, Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430022, China.
2. Department of Neurosurgery, Suizhou Hospital, Hubei University of Medicine, Suizhou, Hubei, 441300, China.
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
Aims: Gliomas are the most common malignant brain neoplasms with high recurrence and lethality rates. Recently, studies have reported that cyclin-dependent kinase 5 (CDK5) is involved in tumorigenesis. Herein, we applied bioinformatics analysis to determine the clinical value of CDK5 in patients with glioma and examined the effects of CDK5 on glioblastoma cell proliferation, apoptosis, and cell cycle in vitro.
Methods: Gene expression profiles containing clinical data of low-grade glioma (LGG) and glioblastoma cohorts were obtained from The Cancer Genome Atlas database and analyzed to determine the association between CDK5 expression and glioma clinicopathological characteristics. Kaplan-Meier survival analysis was performed for prognosis analysis. Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) was used to identify the biological pathways involved in differential CDK5 expression. In vitro experiments were performed to explore the effects of CDK5 on glioma cell functions.
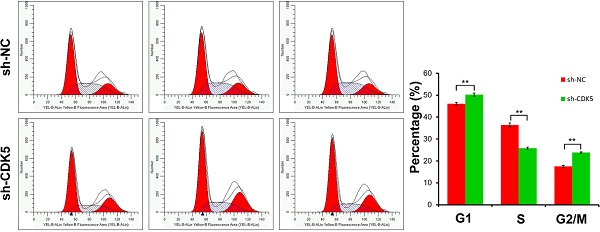
Results: CDK5 expression was substantially higher in glioblastoma than in LGG. GSEA showed that some metabolism-related pathways were associated with the high CDK5 expression phenotype. In vitro experiments showed that CDK5 knockdown impaired cell proliferation and colony formation ability, and induced apoptosis and cell cycle arrest.
Conclusion: CDK5 may act as a potential biomarker of glioma progression and a valid target for glioma therapy.
Keywords: bioinformatics analysis, CDK5, gene set enrichment analysis, glioma, metabolism

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact