3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2021; 12(8):2173-2180. doi:10.7150/jca.50299 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Genome-wide Expression Analysis Identifies the Association between SEC14L2 and Castration-resistant Prostate Cancer Survival
1. Department of Urology, Ruijin Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China.
2. Department of Urology, Shanghai General Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China.
3. Program for Personalized Cancer Care, NorthShore University HealthSystem (Teaching affiliation of University of Chicago), Evanston, IL 60201, USA.
* These authors contributed equally to this study.
Abstract
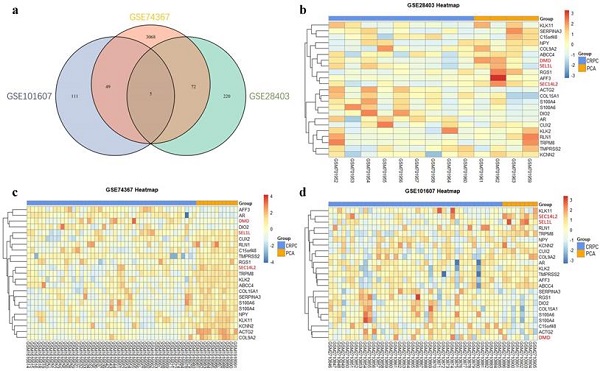
Background: Mechanism of castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) is still unclear. Our objective is to investigate the association between genes expression and CRPC through the genome-wide approach and functional researches.
Methods: Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) between PCa and CRPC tissues were identified using expression profile obtained from Gene Expression Omnibus database (GEO). Survival analysis was performed using online database Gene Expression Profiling Interactive Analysis (GEPIA). Oncomine database was further used to explore the relationship between DEGs expression levels with clinical parameters. After in silico study, SEC14L2-knockdown CRPC cells and normal prostatic epithelial cells were used for in vitro study to verify its biological functions.
Results: A total of 3 consistently changed DEGs (SEC14L2, DMD, SEL1L) were identified correlating with CRPC after cross validation in three independent datasets. Low expression of SEC14L2 was associated with poorer disease-free survival and higher Gleason score than normal/high expression of SEC14L2. SEC14L2 knockdown promoted cell proliferation, migration, invasion as well as cell cycle progression in CRPC cells (all P<0.05) while no significant effects were observed in normal prostatic epithelial cells.
Conclusions: Low expression of SEC14L2 was significantly associated with CRPC, and correlated with PCa aggressiveness and poorer prognosis. SEC14L2 might be a potential biomarker or drug target for CRPC.
Keywords: Expression, Castration-resistant prostate cancer, prognosis.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact