3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2021; 12(7):2065-2072. doi:10.7150/jca.53119 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Co-expression of PD-L1 and HIF-1α predicts poor prognosis in Patients with Non-small Cell Lung Cancer after surgery
Department of Pathology, The Second Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha, Hunan, 410011, China.
Abstract
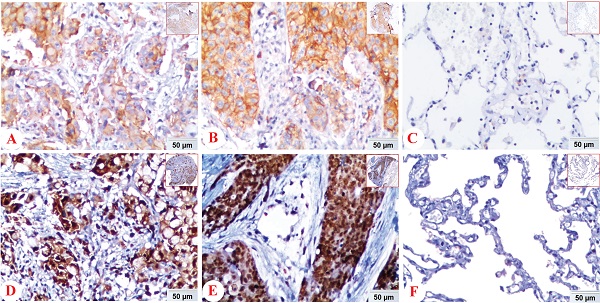
Purpose: PD-L1 is highly expressed in multiple cancers and suppresses anticancer immunity. HIF-1α, as a vital transcription factor, could regulate the proliferation, metastasis, and apoptosis of cancer cells. The aim of this study was to explore the correlation between PD-L1 and HIF-1α protein and further estimate its clinicopathological/prognostic impact on NSCLC patients. Methods: In this study, expression of PD-L1 and HIF-1α protein was detected by immunohistochemistry in tissue microarrays of NSCLC and non-cancerous tissues. Results: Expression of PD-L1 and HIF-1α protein was evidently elevated in NSCLC tissues compared with non-cancerous control lung tissues (both P<0.05). Also, PD-L1 was higher in male, lung SCC patients with lymph node metastasis (all P<0.05). There was a positive link between PD-L1 and HIF-1α in NSCLC (r=0.177, P=0.005). What's more, overall survival of lung ADC patients had to do with PD-L1 and clinical stage, while that of SCC patients was related to HIF-1α, pathological grade and LNM status (all P<0.05). Furthermore, multivariate analysis confirmed that PD-L1 and HIF-1α were considered to be independent prognostic factors for NSCLC patients (both P<0.05). Conclusion: PD-L1 and HIF-1α may serve as attractive independent worse prognostic biomarkers for NSCLC patients and the combined evaluation of PD-L1 and HIF-1α may also be valuable for prognosis judgment. Additionally, expression of PD-L1 was positively correlated with HIF-1α, which may provide evidences for a novel combinational therapy targeting PD-L1 and HIF-1α in NSCLC patients.
Keywords: PD-L1, HIF-1α, biomarkers, Non-small cell lung cancer.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact