3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2021; 12(7):1926-1935. doi:10.7150/jca.53325 This issue Cite
Research Paper
ARRB1 Drives Gallbladder Cancer Progression by Facilitating TAK1/MAPK Signaling Activation
1. Department of Hepato-biliary-pancreatic Surgery, The Affiliated Changzhou No. 2 People's Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, XingLong Road 29#, Changzhou, Jiangsu 213000, P.R. China.
2. Nanjing Medical University, Jiangsu 210000, P.R. China.
3. Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery of Nanjing Drum Tower Hospital, Nanjing Medical University, Jiangsu 210000, China.
* These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
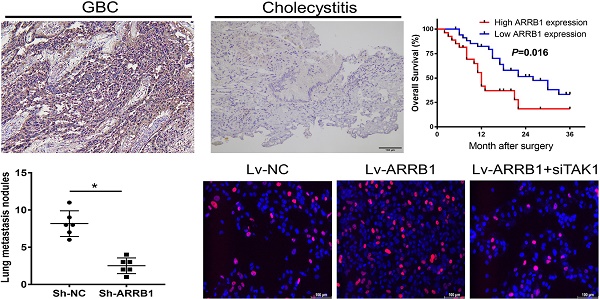
Gallbladder carcinoma (GBC) is the most common malignancy of the biliary tract, with a dismal 5-year survival of 5%. Recently, ARRB1, as a molecular scaffold, has been proposed to participate in the progression of multiple malignancies. However, the effect and regulatory mechanisms of ARRB1 in GBC have not been investigated. Our study aimed to explore the biological functional status and the possible molecular mechanisms of ARRB1 with respect to GBC progression. The survey showed that human GBC tissues exhibited increased levels of ARRB1 compared with normal tissues, and the high expression of ARRB1 was associated with poor prognosis of GBC patients. A series of in vitro and in vivo functional experiments based on knockdown of ARRB1 uncovered that ARRB1 enhanced GBC cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. Furthermore, we reported that TAK1, a component of the TNF /MAPK pathway, is a vital downstream effector of ARRB1. In addition, siTAK1 could abolish the functional changes between ARRB1 overexpression GBC cells and control ones. Our data revealed that ARRB1 facilitated the carcinogenesis and development of GBC through TNF/TAK1/MAPK axis, suggesting that ARRB1 may be a promising biomarker and treatment target for GBC patients.
Keywords: ARRB1, TNF-α, TAK1, Gallbladder carcinoma.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact