3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2024; 15(5):1429-1441. doi:10.7150/jca.92521 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Disruption of Autophagic Flux and Treatment with the PDPK1 Inhibitor GSK2334470 Synergistically Inhibit Renal Cell Carcinoma Pathogenesis
1. Department of Urology, Jiangxi Cancer Hospital, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang Medical College, Jiangxi Clinical Research Center for Cancer, Nanchang, Jiangxi 330000, China.
2. Department of Pathology, Jiangxi Cancer Hospital, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang Medical College, Jiangxi Clinical Research Center for Cancer, Nanchang, Jiangxi 330000, China.
3. Department of Urology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University, Nanchang, Jiangxi 330000, China.
* Equal contribution.
Abstract
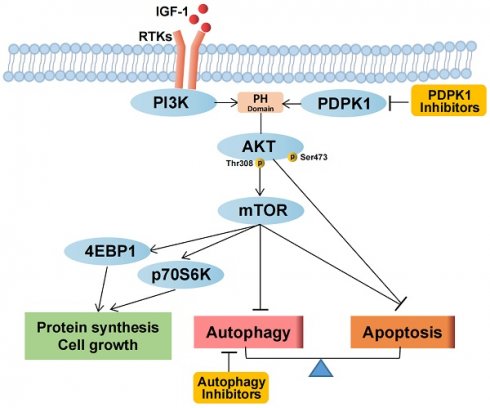
Background: Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) frequently exhibits activating PI3K-Akt-mTOR pathway mutations. 3-Phosphoinositide-dependent kinase 1 (PDPK1 or PDK1) has been established to play a pivotal role in modulating PI3K pathway signaling. mTOR is the main autophagy-initiating factor. However, limited advances have been made in understanding the relationship between PDPK1 and autophagy in RCC.
Methods: GSK2334470 (GSK470), a novel and highly specific inhibitor of PDPK1, was selected to investigate the anticancer effects in two RCC cell lines. Cell growth was assessed by CCK-8 test and colony formation. Changes in the protein levels of key Akt/mTOR pathway components and apoptosis markers were assessed by Western blotting. Autophagy was assessed by using LC3B expression, transmission electron microscopy, and a tandem mRFP-EGFP-LC3 construct. The effect of PDPK1 and autophagy inhibitor chloroquine in RCC in vivo was examined in a mouse tumor-bearing model.
Results: GSK470 significantly inhibited cell proliferation and induces apoptosis in A498 and 786-O RCC cells. GSK470 downregulates the phosphorylation of PDPK1, thereby inhibiting downstream phosphorylation of Akt1 at Thr308 and Ser473 and mTOR complex 1 (mTORC1) activity. Treatment with insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) partially restored GSK470-induced behaviors/activities. Interestingly, treatment of A498 and 786-O cells with GSK470 or siPDPK1 induced significant increases in the hallmarks of autophagy, including autophagosome accumulation, autophagic flux, and LC3B expression. Importantly, GSK470 and chloroquine synergistically inhibited the growth of RCC cells in vitro and in xenograft models, supporting the protective role of autophagy activation upon blockade of the PDPK1-Akt-mTOR signaling pathway.
Conclusion: Our study provides new insight into PDPK1 inhibition combined with autophagy inhibition as a useful treatment strategy for RCC.
Keywords: Renal cell carcinoma, 3-Phosphoinositide-dependent kinase 1, Autophagy, PI3K-Akt-mTOR pathway, Targeted therapy

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact