Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2024; 15(4):990-998. doi:10.7150/jca.90321 This issue Cite
Research Paper
MiRNA-766-3p inhibits gastric cancer via targeting COL1A1 and regulating PI3K/AKT signaling pathway
1. School of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 201203, China.
2. Department of Gastroenterology, Yueyang Hospital of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 200437, China.
3. Central Laboratory, Shanghai Skin Disease Hospital, School of Medicine, Tongji University, Shanghai 200443, China.
4. Shanghai Institute of Stem Cell Research and Clinical Translation, Shanghai 200120, China.
* These authors contributed equally to this work and should be considered co-first authors.
Abstract
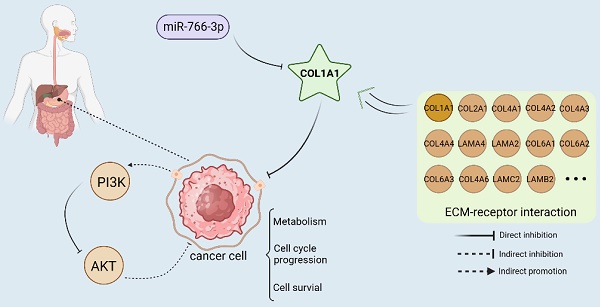
Objective MiRNA-766-3p has been shown to be associated with a variety of cancers. However, few studies have been done in gastric cancer (GC). This study explores the mechanism of miR-766-3p in GC.
Methods The potential targets of microRNA (miRNA) were predicted using Tarbase and Targetscan databases. The results are intersected with differential genes (DEGs) (fold change > 1.5, P < 0.05) in gastric cancer to obtain potential core targets. The hub targets screened by constructing PPI networks (degree > 5, expression > 0.5). Validating the differential expression and expression in immunohistochemistry of these targets through the database. And the binding sites between miRNAs and mRNAs were verified using dual-luciferase Assay. Finally, qRT-PCR and Western Blot experiments were conducted to validate the hub targets and signal pathways.
Results The potential hub targets from the PPI network were THBS2, COL1A1, FGG, FGB, and PLAU. Combining database, luciferase Assay and experimental validation, miR-766-3p can sponge COL1A1 and it plays the most important role in gastric cancer progression. In GC, COL1A1 was upregulated and the enrichment analysis revealed that COL1A1 regulates PI3K/AKT signal pathway, and AKT is also highly expressed in gastric cancer.
Conclusion The miR-766-3p can inhibit the progression of gastric cancer by targeting COL1A1 and regulating the PI3K/AKT signal pathway. It could be a potential therapy option for the GC.
Keywords: MiRNA-766-3p, COL1A1, PI3K/AKT signal pathway, Gastric cancer.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact