3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2023; 14(10):1725-1735. doi:10.7150/jca.84654 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Targeting ESM1/ VEGFα signaling axis: a promising therapeutic avenue for angiogenesis in cervical squamous cell carcinoma
1. Department of Pathology, Taihe Hospital, Hubei University of Medicine, Shiyan 442000, China.
2. Department of Immunology, Nankai University School of Medicine, Tianjin 300110, China.
3. Department of obstetrics and gynecology, Sinopharm Dongfeng General Hospital, Hubei University of Medicine, Shiyan 442008, China.
† These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
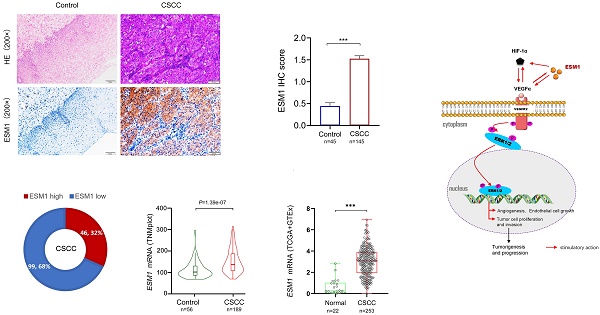
Background: Endothelial-specific molecule 1 (ESM1) dysregulation is widespread in various malignancies. However, the exact significance of ESM1 in cervical squamous cell carcinoma (CSCC) is not yet well understood.
Methods: The expression of ESM1 in CSCC was probed by immunohistochemistry (IHC) assay using human specimens and validated and explored ESM1 in CSCC based on TNMplot and TCGA (The Cancer Genome Atlas Program) data repository. Further, the GSEA analysis and in vitro experiments of human CSCC cell lines, including SiHa and ME-180, were performed to investigate the masked molecular mechanisms of ESM1 in CSCC.
Results: ESM1 was overexpressed in clinical CSCC tissues compared with paracancer controls, was an independent prognostic factor and was associated with poor prognosis in CSCC patients. These findings were further confirmed in the TNMplot and TCGA datasets. Furthermore, GSEA analysis revealed that the ESM1 high expression group was significantly enriched in carcinoma angiogenesis and the VEGFα signaling pathway. In addition, in vitro assays with human CSCC cell lines, including SiHa and ME-180, demonstrated that knockdown of ESM1 expression inhibited tumor cell proliferation, migration and invasion, resulting in attenuated VEGFα expression and blocked phosphorylation of VEGFR2 and ERK-1/2.
Conclusion: In CSCC patients, ESM1 was considerably overexpressed. Upregulation of ESM1 is predictive of poor clinical outcomes in CSCC. Furthermore, ESM1 overexpression promoted carcinoma angiogenesis and CSCC progression through the VEGF/ERK signaling pathway. Hence, ESM1 and associated genes might be useful prognostic biomarkers or therapeutic targets for CSCC individuals.
Keywords: ESM1, cervical squamous cell carcinoma, carcinoma angiogenesis, VEGFα

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact