3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2023; 14(9):1673-1688. doi:10.7150/jca.83466 This issue Cite
Research Paper
LncRNA LINC01569 promotes M2 macrophage polarization to accelerate hypopharyngeal carcinoma progression through the miR-193a-5p/FADS1 signaling axis
1. Department of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery, The First Affiliated Hospital of Fujian Medical University, Fuzhou 350004, Fujian Province, China.
2. Department of Head and neck surgery, Clinical Oncology School of Fujian Medical University, Fujian Cancer Hospital, Fuzhou 350014, Fujian Province, China.
3. Fujian Key Laboratory of Rehabilitation Technology. Fuzhou 350003, Fujian Province, China.
4. Gastrointestinal Endoscopy Department, Rehabilitation Hospital Affiliated to Fujian University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Fuzhou 350003, Fujian Province, China.
5. Department of Abdominal Oncology, Clinical Oncology School of Fujian Medical University, Fujian Cancer Hospital, Fuzhou 350014, Fujian Province, China.
6. Department of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery, National Regional Medical Center, Binhai Campus of the First Affiliated Hospital, Fujian Medical University, Fuzhou 350212, Fujian Province, China.
* These authors contribute equally to this study.
Abstract
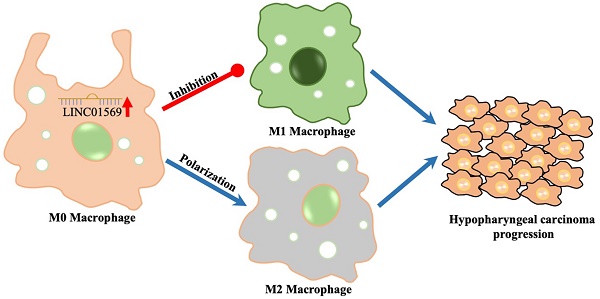
Background: Long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) LINC01569 plays an important role in regulating the tumor microenvironment (TME) and macrophage polarization. However, whether it participates in the progression of hypopharyngeal carcinoma by regulating the TME remains unclear.
Methods: An online database was used to analyze clinical data. Macrophage polarization was detected using qRT-PCR and flow cytometry. In vivo experiments were performed using tumor-bearing nude mice. A co-culture system of hypopharyngeal carcinoma cells and macrophages was used to explore the interactions between the two cell types.
Results: LINC01569 enhancement was observed in hypopharyngeal carcinoma tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs). In IL4-induced M2 macrophages, the expression of LINC01569 increased, while LINC01569 expression declined significantly in LPS-induced M1 macrophages. SiRNA-mediated downregulation of LINC01569 inhibits IL4-induced M2 macrophage polarization. Using online databases and a dual-luciferase reporter, miR-193a-5p was confirmed as a potential downstream sponge of LINC01569. MiR-193a-5p expression decreased in IL4-mediated M2 macrophages, which was restored by LINC01569 downregulation. Additionally, LINC01569 inhibition-mediated blocking of M2 macrophage polarization was moderately abolished by transfection with the miR-193a-5p inhibitor. Fatty acid desaturase 1 (FADS1) was verified as a downstream target of miR-193a-5p, and LINC01569 downregulation-mediated inhibition of FADS1 was blocked by miR-193a-5p mimics. Importantly, LINC01569 downregulation-mediated decline in M2 macrophage polarization was abolished by miR-193a-5p mimics, which was further reversed by FADS1 knockdown. Implantation of a mixture of FaDu cells and IL4-induced macrophages promoted tumor growth and proliferation, which were abrogated by the knockdown of LINC01569 in macrophages. Using an in co-culture system of FaDu cells and macrophages in vitro, M2 macrophage-regulated cell growth and apoptosis of FaDu cells were found to be mediated by the LINC01569/miR-193a-5p signaling axis.
Conclusion: LINC01569 is highly expressed in the TAMs of hypopharyngeal carcinoma. LINC01569 downregulation restrains macrophages from polarizing toward M2 through the miR-193a-5p/FADS1 signaling axis, thereby helping tumor cells escape inherent immune surveillance and promoting the occurrence and development of hypopharyngeal carcinoma.
Keywords: hypopharyngeal carcinoma cancer, LINC01569, miR-193a-5p, FADS1, macrophage polarization.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact