3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2023; 14(9):1562-1570. doi:10.7150/jca.84894 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Endobronchial Radiofrequency Ablation for pulmonary nodules with Radial-Ebus and Navigation: Pros and Cons
1. Pulmonary Department, General Clinic Euromedica, Thessaloniki, Greece.
2. Sana Clinic Group Franken, Department of Cardiology / Pulmonology / Intensive Care / Nephrology, ''Hof'' Clinics, University of Erlangen, Hof, Germany.
3. Department of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, The Affiliated Huaian No.1 People's Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Huai'an 223300, China.
4. Pulmonary Department, ``G. Papanikolaou`` General Hospital, Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, Thessaloniki, Greece.
5. 3 rd Surgery Department, AHEPA University Hospital, Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, Thessaloniki, Greece.
6. Oncology Department, University General Hospital of Larissa, Larissa, Greece.
7. Oncology Department, General Hospital of Volos, Greece.
8. Private Oncology Clinic, Oncoderm, Ioannina, Greece.
9. Surgery Department, Genesis Private Clinic, Thessaloniki, Greece.
10. Oncology Department, General Hospital of Rhodes, Rhodes, Greece.
11. 1st Department of Surgery, Attica General Hospital "Sismanogleio - Amalia Fleming", Athens, Greece.
12. Second Department of Surgery, University Hospital of Alexandroupolis, Medical School, Democritus University of Thrace, Alexandroupolis, Greece.
13. Oncology Department, University General Hospital of Larissa, Larissa, Greece.
14. Department of Pharmacology & Clinical Pharmacology, School of Medicine, Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, Thessaloniki, Greece.
15. Department of Anatomy, University of Cyprus Medical School, Cyprus, Greece
16. Department of Medicine, Laboratory of Medical Biology and Genetics, Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, Thessaloniki, Greece.
17. Department of Respiratory & Critical Care Medicine, Changhai Hospital, the Second Military Medical University, Shanghai, P. R. China.
*Paul Zarogoulidis and Wei Chen contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
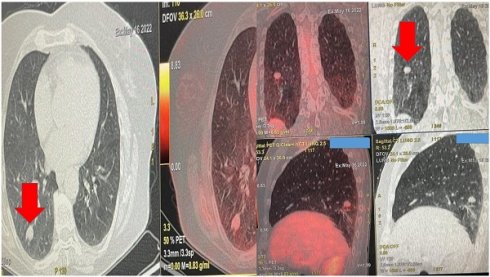
Introduction: Pulmonary nodules are common in the everyday clinical practice. There is always a diagnostic issue with this imaging finding. Based on the size we can use a variety of imaging and diagnostic techniques. Moreover; in the case of primary lung cancer or metastasis we can use radiofrequency ablation endobronchially.
Patients and Methods: We used the radial-endobronchial ultrasound with C-arm and Archemedes, Bronchus electromagnetic navigation in order to acquire biopsy sample and we also used rapid on-site evaluation as a rapid diagnosis for pulmonary nodules. After rapid diagnosis we used the radiofrequency ablation catheter in order to ablate central pulmonary nodules.
Results: Both techniques provide efficient navigation, however, with the Bronchus system less time is needed. The new radiofrequency ablation catheter provides efficient results in central lesions with low watts ≤40.
Conclusion: We provided in our research a protocol to diagnose and treat such lesions. Future larger studies will provide more data on this subject.
Keywords: bronchoscopy, rapid on-site evaluation, ROSE, radiofrequency ablation, radial-ebus, C-arm, lung cancer.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact