3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2023; 14(7):1242-1256. doi:10.7150/jca.83863 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Activation of the HNRNPA2B1/miR-93-5p/FRMD6 axis facilitates prostate cancer progression in an m6A-dependent manner
1. Clinical Medical Center of Urology, Shanghai General Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China.
2. Institute of Urology, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China.
3. Cancer Center, Shanghai General Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China.
# These authors contributed equally to this study.
Abstract
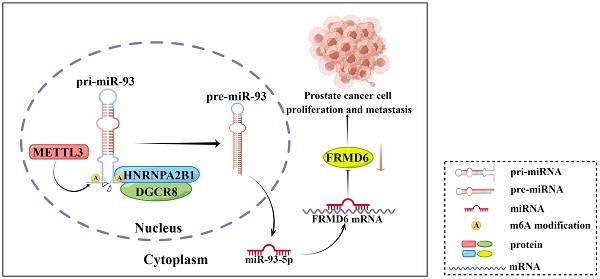
It is becoming increasingly clear that N6-methyladenosine (m6A) plays a key role in post-transcriptional modification of eukaryotic RNAs in cancer. The regulatory mechanism of m6A modifications in prostate cancer is still not completely elucidated. Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A2/B1 (HNRNPA2B1), an m6A reader, has been revealed to function as an oncogenic RNA-binding protein. However, its contribution to prostate cancer progression remains poorly understood. Here, we found that HNRNPA2B1 was highly overexpressed and correlated with a poor prognosis in prostate cancer. In vitro and in vivo functional experiments demonstrated that HNRNPA2B1 knockout impaired proliferation and metastasis of prostate cancer. Mechanistic studies indicated that HNRNPA2B1 interacted with primary miRNA-93 and promoted its processing by recruiting DiGeorge syndrome critical region gene 8 (DGCR8), a key subunit of the Microprocessor complex, in an METTL3-dependent mechanism, while HNRNPA2B1 knockout significantly restored miR-93-5p levels. HNRNPA2B1/miR-93-5p downregulated FERM domain-containing protein 6 (FRMD6), a cancer suppressor, and enhanced proliferation and metastasis in prostate cancer. In conclusion, our findings identified a novel oncogenic axis, HNRNPA2B1/miR-93-5p/FRMD6, that stimulates prostate cancer progression via an m6A-dependent manner.
Keywords: HNRNPA2B1, Prostate cancer, m6A, miR-93-5p, FRMD6

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact