3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2023; 14(3):393-402. doi:10.7150/jca.77322 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Platycodin D confers oxaliplatin Resistance in Colorectal Cancer by activating the LATS2/YAP1 axis of the hippo signaling pathway
1. Department of Chinese Medicine, Hualien Tzu Chi Hospital, Buddhist Tzu Chi Medical Foundation, Tzu Chi University, Hualien, Taiwan
2. Integration Center of Traditional Chinese and Modern Medicine, Hualien Tzu Chi Hospital, Buddhist Tzu Chi Medical Foundation, Hualien, Taiwan
3. Department of Bioinformatics and Medical Engineering, Asia University, Taichung, Taiwan
4. Department of Biological Science and Technology, College of Life Sciences, China Medical University, Taichung, Taiwan
5. Ph.D. Program for Biotechnology Industry, China Medical University, Taichung 406, Taiwan
6. Department of Hematology and Oncology, Hualien Tzu Chi Hospital, Buddhist Tzu Chi Medical Foundation, Hualien, Taiwan
7. School of Medicine Tzu Chi University, 701, Section 3, Chung-Yang Road, Hualien 97004, Taiwan
8. Center of Stem Cell & Precision Medicine, Hualien Tzu Chi Hospital, Buddhist Tzu Chi Medical Foundation, Hualien, Taiwan
9. Chinese Medicine, Hualien Tzu Chi Hospital, Buddhist Tzu Chi Medical Foundation, Tzu Chi University, Hualien, Taiwan
10. Department of Medical Laboratory Science and Biotechnology, China Medical University, Taichung, Taiwan
11. School of Medical Laboratory and Biotechnology, Chung Shan Medical University, Taichung, Taiwan
12. Clinical Laboratory, Chung Shan Medical University Hospital, Taichung 402, Taiwan
13. Laboratory of Exercise Biochemistry, University of Taipei, Taipei, Taiwan
14. Department of Kinesiology and Health Science, College of William and Mary, Williamsburg, VA, USA
15. Department of Surgery, Division of Colorectal Surgery, Taichung Veterans General Hospital, Taichung, Taiwan
16. Faculty of Medicine, National Yang-Ming University, Taipei, Taiwan.
17. Cardiovascular and Mitochondria related diseases research center, Hualien Tzu Chi Hospital, Hualien 970, Taiwan
18. Graduate Institute of Biomedicine, China Medical University, Taichung, Taiwan
19. Department of Biotechnology, Asia University, Taichung 413, Taiwan
20. Center of General Education, Buddhist Tzu Chi Medical Foundation, Tzu Chi University of Science and Technology, Hualien 970, Taiwan
21. Department of Medical Research, China Medical University Hospital, China Medical University, Taichung 404, Taiwan
Abstract
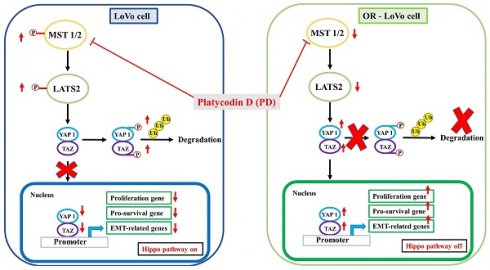
Oxaliplatin-based therapy is used as a first-line drug to treat metastatic colorectal cancer. However, long-term and repeated drug treatment resulted in drug resistance and the failure of chemotherapy. Various natural compounds were previously reported to act as chemosensitizers to reverse drug resistance. In this study, we found that platycodin D (PD), a saponin found in Platycodon grandiflorum, inhibited LoVo and OR-LoVo cells proliferation, invasion, and migration ability. Our results indicated that combined treatment of oxaliplatin with PD dramatically reduced the cellular proliferation in both LoVo and OR-LoVo cells. Furthermore, treatment with PD dose-dependently decreased LATS2/YAP1 hippo signaling and survival marker p-AKT expression, as well as increased cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor proteins such as p21 and p27 expression. Importantly, PD activates and promotes YAP1 degradation through the ubiquitination and proteasome pathway. The nuclear transactivation of YAP was significantly reduced under PD treatment, leading to transcriptional inhibition of the downstream genes regulating cell proliferation, pro-survival, and metastasis. In conclusion, our results showed that PD is suitable as a promising agent for overcoming oxaliplatin-resistant colorectal cancer.
Keywords: Oxaliplatin, Drug resistance, Platycodin, Cell cycle, metastasis

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact