3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2022; 13(14):3584-3592. doi:10.7150/jca.78098 This issue Cite
Research Paper
LHPP suppresses gastric cancer progression via the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway
1. Department of Oncology, Xi'an Gaoxin Hospital, Xi'an, Shaanxi, China.
2. Department of Surgical Oncology, Shaanxi Provincial People's Hospital, Xi'an, Shaanxi, China.
3. The Third Affiliated Hospital, School of Medicine, Xi'an Jiaotong University, Xi'an, Shaanxi, China.
Abstract
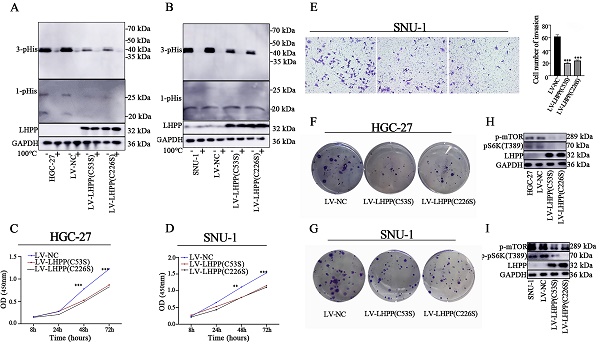
Emerging evidence has revealed the anti-oncogenic role of LHPP in several malignancies. The current study aims to explore the underlying mechanism of LHPP in gastric cancer (GC). We used the TCGA and GEO databases to investigate the expression profile, prognostic value, and cellular function of LHPP in GC. LHPP expression pattern were further verified using clinical samples by immunohistochemistry and western blot analysis. Moreover, stable cancer cell lines with LHPP overexpression or knockdown were established. CCK-8 assay, colony formation assay, transwell assay, qRT-PCR, and western blot analysis were performed to uncover the underlying mechanism concerning LHPP during the progression of GC. The present study revealed that LHPP was down-regulated in GC cell lines and tissue samples at both mRNA and protein level. LHPP inhibited GC cells proliferation, migration, invasion, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in vitro. Mechanically, LHPP overexpression led to decreased level of PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway phosphorylation, while LHPP depletion produced opposite results. Moreover, our data indicated that the enzymatic active site of LHPP is neither the cysteine residue at position 226 nor at position 53 in GC. Overall, our study demonstrated that LHPP function as a tumor suppressor gene in GC by regulating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway.
Keywords: LHPP, Gastric cancer, EMT, the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact