3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2022; 13(9):2740-2750. doi:10.7150/jca.64765 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Increased DNA Polymerase Epsilon Catalytic Subunit Expression Predicts Tumor Progression and Modulates Tumor Microenvironment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
1. Department of Integrated Medicine, Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing, 210000, China
2. Department of Radiology, Fudan University Shanghai Cancer Center, Shanghai, China
3. Department of Urology, Fudan University Shanghai Cancer Center, School of Life Sciences, Fudan University, Shanghai, China
4. Department of Urology, PKUCare CNOOC Hospital,Tianjin,300452, China
5. Affiliated Hospital of Youjiang Medical University for Nationalities, Guangxi, China
6. School of Integrated Chinese and Western Medicine, Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing 210023, China
7. Department of Interventional Oncology, Renji Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China
*Equal contribution
Abstract
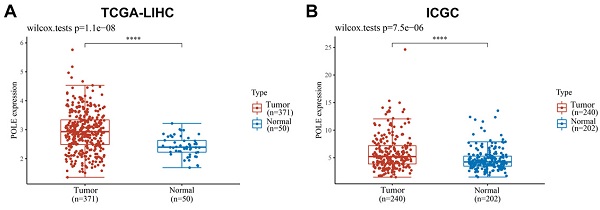
Backgrounds: Liver hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most common cancers worldwide, and POLE, playing an important role in maintaining genetic stability, is closely connected with cancer prognosis. This study aimed to explore the significance role of POLE in HCC prognosis, clinical treatment and tumor immune microenvironment based on large-scale multiply cohorts.
Methods: First, we found that the expression of POLE was prominently higher in tumor tissues than in normal tissues, and was closely related to clinical stage, grade and patient outcomes. Second, we found that patients with high POLE expression had significantly aggressive progression, indicating effective predictive role of POLE expression for Asian, male, low-risk HCC patients. Additionally, POLE mutation frequency was detected in several datasets with available genomic-wide data.
Results: 130 HCC samples from real-world Renji cohort were included to demonstrate that elevated POLE expression was significantly connected to the invasive progression and poor prognosis. More importantly, the expression of POLE was closely related to the anti-tumoral activity of immune cells and immune checkpoints expression, suggesting a bright prospect of POLE as a predictive biomarker in immunotherapy.
Conclusion: In conclusion, this study revealed that high expression of POLE significantly correlated to the malignant progression, poor prognosis and anti-tumoral activity of immune cells in HCC. Thus, POLE could function as a biomarker for the early diagnosis, prognosis, immune-excluded tumor microenvironment and response to immunotherapy of HCC.
Keywords: POLE, liver hepatocellular carcinoma, tumor immune microenvironment, prognosis

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact