3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2021; 12(17):5320-5330. doi:10.7150/jca.58697 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Repression of the miR-627-5p by histone deacetylase 3 contributes to hypoxia-induced hepatocellular carcinoma progression
1. Department of Emergency, The First Affiliated Hospital of Xi'an Jiaotong University, Xi'an 710061, China.
2. Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery, The First Affiliated Hospital of Xi'an Jiaotong University, Xi'an 710061, China.
3. The Key Laboratory of Tumor Molecular Diagnosis and Individualized Medicine of Zhejiang Province, Zhejiang Provincial People's Hospital, Affiliated People's Hospital, Hangzhou Medical College, Hangzhou 310014, China.
Abstract
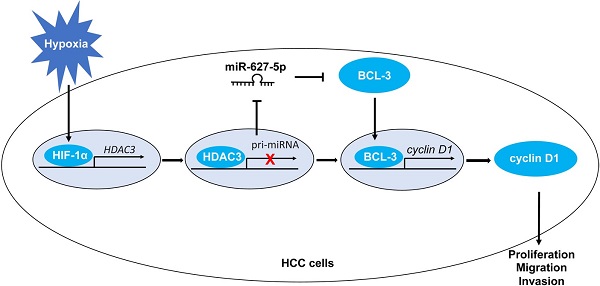
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most common solid tumors globally. Our previous studies revealed that miR-627-5p suppresses HCC progression via targeting BCL3/CCND1 pathway. However, the molecular mechanism by which miR-627-5p was downregulated in HCC remains to be further elucidated. As a hallmark of solid tumors, hypoxia results in the rapid growth, strongly potential invasion and high frequent metastasis of cancer cells. Hypoxia-inducible factors (HIFs), mainly including HIF-1 and HIF-2, are the classical transcription factors which mediate hypoxia-related gene transcription. Here, we demonstrated that miR-627-5p was repressed by hypoxia in a HIF-1-dependent manner in HCC cells. But HIF-1 regulated miR-627-5p expression not directly through the hypoxia-response element (HRE) sites of MIR627 gene. In contrast, histone deacetylase 3 (HDAC3) was identified as a HIF-1 target gene, and the occupancy of HIF-1 to HRE site was essential for hypoxia-mediated HDAC3 induction. And upregulated HDAC3 was closely related to the malignant clinical and pathological characteristics and worse prognosis of HCC. Furthermore, HDAC3-mediated histone deacetylation in promoter region of MIR627 was critical for hypoxia-mediated miR-627-5p repression. And miR-627-5p mediated the effects of hypoxic condition on HCC progression. Thus, this study has revealed that miR-627-5p was repressed by hypoxia under the mediation of HDAC3 in HCC, and there existed a HIF-1α/HDAC3/miR-627-5p/BCL3/CCND1 signal pathway in HCC.
Keywords: Hepatocellular carcinoma, Hypoxia, HDAC3, miR-627-5p, Histone deacetylation

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact