3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2021; 12(10):3067-3076. doi:10.7150/jca.54759 This issue Cite
Research Paper
miR-369 inhibits Liver Cancer progression by targeting ZEB1 pathway and predicts the prognosis of HCC patients
1. Department of Gastroenterology, Shanghai General Hospital, School of Medicine, Shanghai Jiao Tong University. Shanghai, 200080, China.
2. Department of General Surgery, Cao County People's Hospital, Heze, Shandong province, 274400, China.
3. Department of Gastroenterology, Rui Jin Hospital, School of Medicine, Shanghai Jiao Tong University. Shanghai, 200025, China.
#Co-first authors with equal contributions to this work.
Abstract
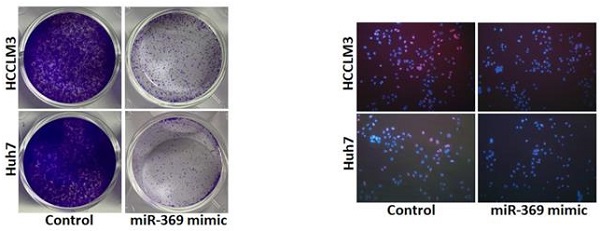
Increasing evidences show that microRNAs (miRNAs) are involved in the regulation of tumorigenesis, progression, recurrence and drug resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). miR-369 works as a tumor suppressor in both lung cancer and thyroid cancer. However, the potential biological function of miR-369 in HCC is unknown. Herein, we for first found that miR-369 expression was downregulated in HCC tissues and predicted the poor prognosis of HCC patients. Forced miR-369 expression inhibited the proliferation and metastasis of HCC cells in vitro and in vivo. Mechanically, bioinformatics and luciferase reporter analysis identified Zinc finger E-box binding homeobox 1 (ZEB1) as a direct target of miR-369 in HCC cells. miR-369 overexpressing downregulated the ZEB1 mRNA and protein expression in HCC cells. miR-369 expression was negatively associated with ZEB1 expression in human HCC tissues. More importantly, the ZEB1 siRNA diminished the discrepancy of growth and metastasis capacity between miR-369 overexpression HCC cells and control cells.
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma, miR-369, ZEB1, prognosis, progression

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact